High Temperature Creep
High temperature creep refers to the Isothermal deformation of products subjected to stress at high temperature with the change of time. Due to the different external forces, high temperature creep can be divided into high temperature compression creep, high temperature tensile creep, high temperature bending creep and high temperature torsional creep.
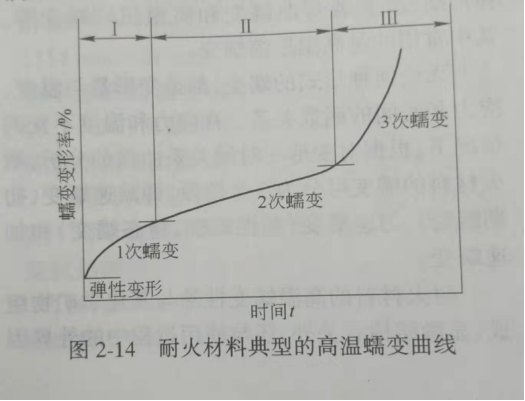
In any form of creep, the amount of deformation is a function of temperature, stress and time. In the case of the constant stress and temperature, the creep of the refractory material can be divided into three stages, namely, deceleration creep (initial creep), constant-speed creep (viscous creep, steady-state creep) and accelerated creep, based on the analysis of the deformation-time relationship curve. The high-temperature creep property of the refractory material is related to the external factors in the use process, such as the use of temperature, pressure, atmosphere, erosion of the refractory material, etc., in addition to its chemical mineral composition and microstructure, such as the use of temperature, pressure, atmosphere, smoke, molten metal, slag, etc. during use.
In order to improve the peristaltic properties of refractories, it is important to improve their chemical mineral composition and microstructure. Measures such as improving the purity of raw materials, formulating reasonable particle gradation, increasing molding pressure, properly increasing firing temperature and prolonging holding time can be taken.
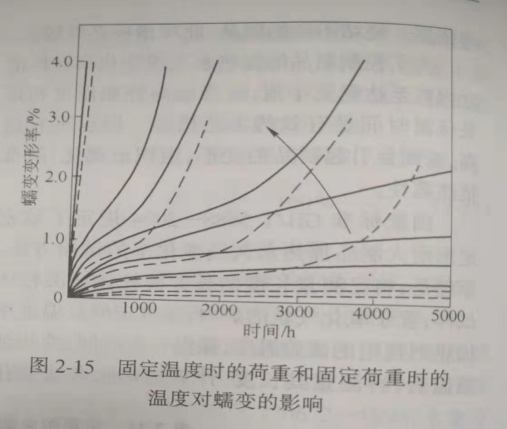
By measuring the creep of refractories, the microstructure changes of refractories caused by stress at high temperature can be studied, the quality of products can be inspected and the production process can be evaluated. In addition, by measuring the creep curves of refractory products at different temperatures and loads, the minimum temperature of creep, the creep rate at different temperatures and the deformation characteristics under high temperature stress can be understood, which provides the basis for predicting the changes of refractory products under load in practical application and evaluating the performance of refractory products in kiln design.
The national standard GB/T5073-2005 specifies the test method for compressive creep of refractory products. The principle is that the deformation in the direction of height and the percentage of variation relative to the original height of the sample are recorded at a certain heating rate and constant temperature at a specified test temperature at a constant pressure.
The creep rate is calculated as follows:
P=(Ln-L0)/Li
In the formula, P = creep rate,%;
Li=Original height of sample, mm;
L0 = the height of the sample at the beginning of constant temperature, mm;
The height of Ln= sample after constant temperature n hours, mm.
The typical high temperature creep curves of refractories are shown in Fig. 2 / 14, and the effects of temperature and load on creep are shown in Fig. 2 / 15.