Direct-bonded Magnesia-chrome Bricks
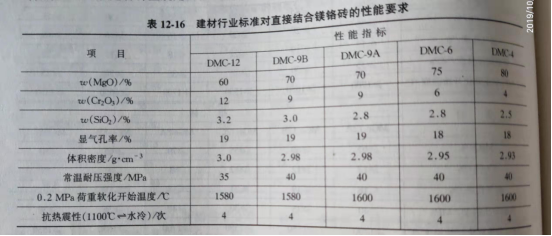
Direct combined magnesia-chromium brick generally refers to the products which are made of chromium ore with low impurity content and pure magnesite at temperature above 1700 ℃. Most of the refractory grains are in direct contact with each other. As a microstructure parameter, direct bonding can be used not only in magnesium-chromium materials, but also in other materials. The concept of direct bonding was first proposed by magnesia-chromium material. In 1959, Laming observed the magnesia-chromium brick sintered and reburned at 1800 ℃ with the help of polarizing microscope. It was found that the magnesia and chromium ore were in close contact with each other, and silicate was squeezed into the corner of the particle. Therefore, this phenomenon is called brucite-square Magnesite and brucite-chromium ore combine directly. The British Ceramic Society organized a number of well-known refractory authorities to discuss his report, praising it as the "technological Revolution in Magnesia-Chrome Brick production process." As a result, J.Laming, A. Hayhurst, H. M. powers and V.Dreser and W.H.Boyer said that bricks fired at temperatures above 1700 ℃ are "high temperature fired bricks." By 1964, it began to be clearly called a "direct combination" brick. However, until now, direct combination is still a qualitative concept, how to identify and evaluate the direct combination of magnesium and chromium Bricks do not form operational unified criteria and quality standards. In metallurgical enterprises and their refractory plants, it is generally considered that the SiO2 content of directly bonded magnesia-chromium bricks should be less than 2% or even 1%, and the load softening temperature should be more than 1650 ℃, preferably more than 1700 ℃. The SiO2 content of directly bonded magnesia-chromium brick stipulated by building materials industry is about 3%, and the load softening temperature is 1600 ℃. The physical and chemical properties of directly bonded magnesia-chromium brick are required by building materials industry standard JC497-1992 (96), as shown in Table 12-16.
The main difference between direct combination magnesia-chromium brick and ordinary magnesia-chromium brick is that the former is made of raw materials with low impurity content and higher temperature.
The main difference between the production process of direct bonded magnesia-chromium brick and ordinary magnesia-chromium brick is that the former is made of raw materials with low impurity content and high temperature.
magnesia used for the production of directly bonded magnesia-chromium bricks, mgo content is generally greater than 95%, preferably greater than 97%, and the particle volume density is about 3.25 g/cm3. the sio2 content in chromium ore is generally limited to less than 3%. when chromium concentrate is used, the sio2 content can be less than 1.0%. According to different needs and uses, sometimes one or two kinds of magnesia and one or two kinds of chromium ore can be selected for batching. The content of Cr \u 2 O \u 3 in cement kiln is 3%~14%. Brick, sometimes the Cr2O3 content is as high as possible (such as 20%). When the pure magnesia and chromium ore co-grinding powder is used as the matrix, the product often expands to produce crack waste when the product is fired. Therefore, the chromium ore content in matrix fine powder should be controlled within the range of firing permission.
The highest firing temperature of directly bonded magnesia-chromium brick varies with the purity and sintering degree of raw materials. The higher the sintering degree of magnesia and the less impurity composition in the burden, the more likely it is to realize ultra-high temperature firing. Directly bonded magnesia-chromium brick, usually fired at more than 1700 ℃.
Because the magnesia (MS95) with 95% MgO content is commonly known as intermediate magnesia, the directly bonded magnesia-chromium brick produced by this magnesia is also called middle-grade magnesia-chromium brick.
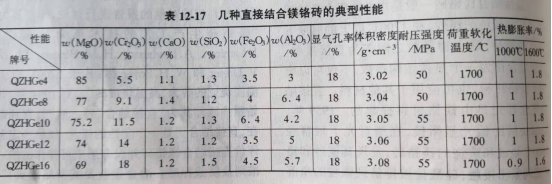
In the chemical composition of directly bonded magnesia-chromium brick, the impurity composition is less and the direct bonding rate between refractory grains is high, so the slag resistance and high temperature performance are good. The thermal shock resistance of directly bonded magnesia-chromium brick is excellent, and the water cooling at 1100 ℃ is 4 times 10 times. Table 12 / 17 lists the typical properties of several directly bonded magnesia-chromium bricks.
Directly combined magnesia-chromium brick is used in cement rotary kiln, steelmaking furnace lining, refining furnace (RH upper slot, lower groove permanent lining, VOD furnace wall), nonferrous metallurgy furnace, glass kiln heat storage chamber, lime kiln, iron mixing furnace and so on.