Carbon Brick for Blast Furnace
The carbonaceous product is a refractory product made of coal tar pitch as a binder by heat-treating anthracite or coke and graphite as main raw material. The carbon network is characterized in that the carbon network is formed by the pyrolysis reaction of the organic bonding agent containing more than 80% of fixed carbon, no sintering property and obvious sintering shrinkage, and the carbon particles and the carbon matrix are combined. Such products include a carbon brick with anthracite or coke as a main component and a graphitized man-made graphite and a semi-graphite carbon brick.
The carbon product has the advantages of high refractoriness, high thermal conductivity, high conductivity, good thermal stability, small linear expansion coefficient, high high-temperature strength, good wear resistance, various acid, alkali, salt and organic solvent corrosion, and is not easy to be corroded by the slag and the molten iron, but is easy to oxidize in an oxidizing atmosphere.
The process of production of the carbonaceous product is substantially similar to other refractory products, but it is necessary to prevent the carbon from being oxidized at a high temperature when producing a carbonaceous product. The roasting of the raw material and the roasting of the product are carried out in a reducing atmosphere. The anthracite shall be burnt before use to eliminate volatile, sulfur and water, and improve the volumetric stability, mechanical strength and oxidation resistance of the anthracite. The coke must be dried first to avoid the difficulty of forming due to the high moisture content and the cracking of the product during the baking process. The asphalt shall also be heated and dewatered. in the production, the raw materials are mixed according to the specified components, are mixed in the heating state, are pressed and formed, The absolute air is roasted in the reduction atmosphere and the volatile matter is removed so that the volume of the volatile matter is stable when it is reheated. The body of calcined carbon products should be machined by planer, milling machine and so on to reach the geometric size specified in the design.
When the graphite product is produced, the baked carbon product also needs to be graphitized at a high temperature of 2400 DEG C or higher. In the production of semi-graphite products, graphite should be introduced in the ingredients.
Due to the high thermal conductivity of the carbonaceous material, the low wettability and low permeability of the molten iron, since the 1950s, the furnace bottom and the furnace hearth of the iron-making blast furnace have a large number of carbonaceous refractory materials, and the furnace waist, the belly and the lower furnace body of the blast furnace also use the carbonaceous refractory material. After the carbonaceous refractory material is adopted, the furnace service of the blast furnace is obviously prolonged, and the burning and wearing of the furnace bottom or the furnace cylinder is seldom occurred. However, with the increasing of the size of the blast furnace and the adoption of the strengthening and smelting technology, the working conditions of the furnace lining material are getting worse and more, so that the lining material has higher requirements. In the late 1970s and the late 1980s, some new variety of high-furnace-carbon bricks appeared, such as through the impregnated high-density carbon brick, the semi-graphite carbon brick with a small amount of silicon carbide is added, the semi-graphite-silicon carbide carbon brick with a small amount of silicon carbide is added, and the microporous carbon brick and the high-temperature hot-pressing carbon brick which are produced after pure silicon, silicon carbide and aluminum oxide are added, And the self-baking carbon brick which is produced by adopting the vibration forming process is not roasted, and after the blast furnace is built into the blast furnace, the whole self-baking carbon brick is roasted by the baking oven and the heat at the initial stage of operation.
Production of blast furnace carbon brick more use anthracite as raw materials, in which ash, volatile matter varies from place of origin, ash is generally 5%, volatile matter 8%, in advance need to be heated in a vertical electric furnace treatment. Other raw materials include artificial graphite and special additives (metal and oxide powder), which are heat-treated dehydrated coal tar pitch.
Ordinary blast furnace carbon brick is used to build medium blast furnace with low smelting strength and 1000~2500m3 volume. High quality anthracite (calcination temperature is about 1250 ℃) is used as the main raw material, and a certain amount of metallurgical coke and graphite crushing are added. After extrusion, the billet should be roasted in the calciner at a temperature above 1100 ℃. After calcination, the milling machine and planer are used for mechanical processing according to the drawings provided by the user. The processed carbon brick is pre-installed in the factory and checked the gap between adjacent blocks, which is qualified and sent to the user.
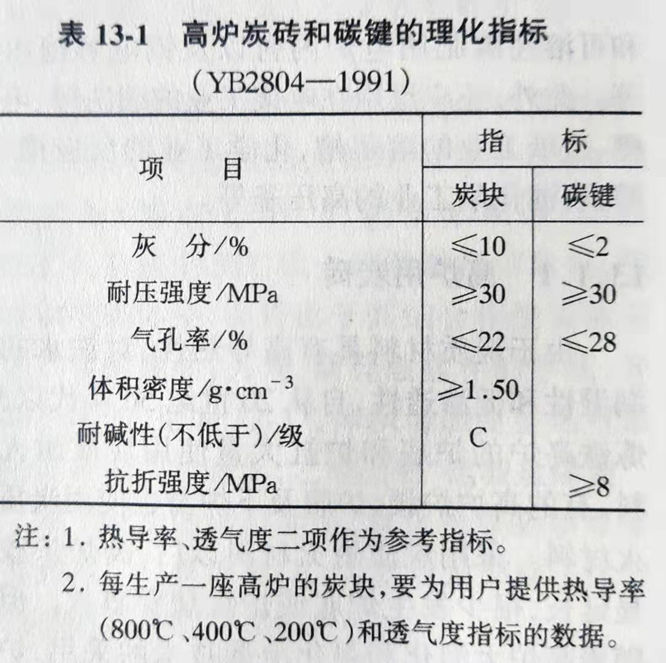
The metallurgical industry standard YB2804-1991 specifies the physical and chemical indexes of blast furnace common carbon bricks, which are shown in Table 13- 1, and the allowable deviation of size and shape quality are also stipulated.
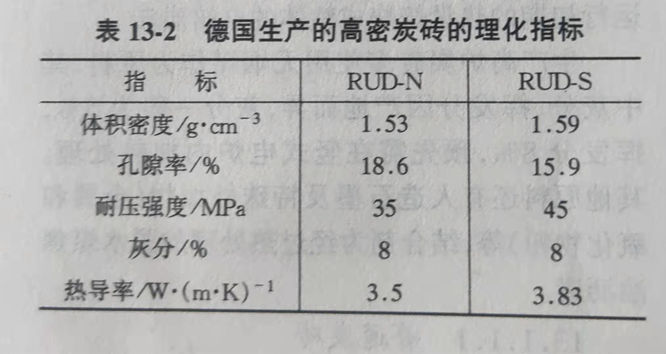
If ordinary carbon brick is dipped with coal tar pitch once, the volume density and mechanical strength of ordinary carbon brick can be improved obviously, which is called high density carbon brick. The porosity of high density carbon brick is reduced, which can reduce the penetration of molten iron or slag. It is used to build blast furnace lining full of furnace bottom or unstrengthened smelting. The physical and chemical properties of ordinary carbon brick (RUD-N) and high density carbon brick (RUD-S) made in Germany are shown in Table 13-2.
In the roasting process (single side heating condition), the volatile matter of coal tar pitch produces reverse movement, and the pyrolysis carbon is formed in the pores of the working hot end matrix and fills the pores, which makes the brick "self-compact".
It can absorb the temperature stress produced by the furnace lining when the furnace lining is heated up, and alleviate the damage of the thermal stress to the furnace lining.
Heterogeneous graphitization transformation is produced under the catalysis of high temperature slag iron and other media in the furnace, which improves the thermal conductivity and chemical corrosion resistance of the lining, and makes the solidification isotherm of molten iron at 1150 ℃ migrate to the furnace.
Due to the characteristics of self-baked carbon brick and the qualitative change in the furnace, the stability and durability of the lining are finally improved, so that the self-baked carbon brick can be widely used in small and medium-sized blast furnaces, and good technical and economic results are obtained. The use of semi-graphite self-baked carbon brick in large blast furnace can reduce the melting index of molten iron, improve the thermal conductivity, improve the resistance to alkali erosion, enhance the oxidation resistance, improve the scour wear resistance and reduce the residual shrinkage.
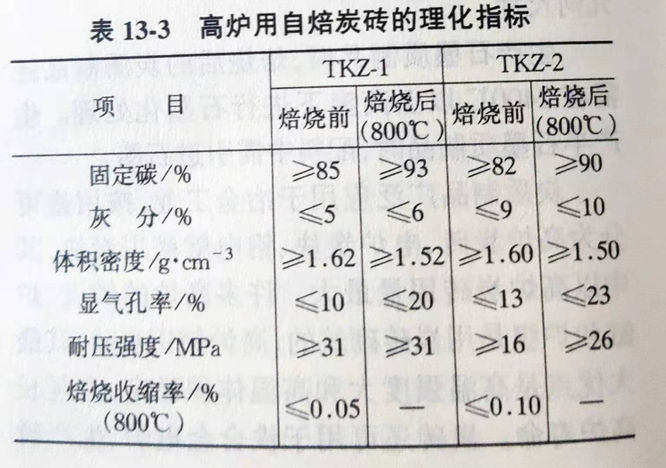
The current YB2804-1991 standard specifies the shape size, size allowable deviation, physical and chemical standard and surface quality of self-baked carbon brick. The self-baked carbon bricks for blast furnace are divided into TKZ-1 and TKZ-2 according to their physical and chemical standards. The physical and chemical indexes are shown in Table 13-3.