Cast Mullite
The melting and casting mullite brick is mainly made of high bauxite or industrial alumina, clay or silica, melted in electric arc furnace, then cast and annealed. The main mineral composition of mullite is mullite.
Form
The mullite composition is 3Al2O32SiO22Al2O3 and SiO2. the melting temperature is about 1827 ℃ and the hardness is high. When the crystallization is cooled by high temperature solution, there will be a coarse and uneven crystallization tendency, which will easily cause cracks in the melting and casting products. When the eutectic mixture is composed of eutectic mixture, the molten liquid has good flowability after melting. Uniform and fine crystallization can be formed during crystallization of mullite, which reduces the possibility of cracks in castings. Therefore, the composition of mullite castings should be 79 / 21:00 in Al2O3/SiO2. However, the existence of raw materials must also be taken into account in production.
The rest of the magazines cannot be removed by reduction, mainly into the melt and in the glass phase.
Raw Material
High bauxite, industrial alumina and clay are usually selected as raw materials. When high bauxite and bauxite are used, the Al2O3/SiO2 ratio should be more than 3.2, Fe _ 2O _ 3 is less than 1.5%, TIO _ 2 is less than 3.0%, Cao is less than 1.0%. Bauxite raw materials should be pre-burned to remove structural water in order to avoid explosion and spatter when water vapor is centrally decomposed and removed in EAF.
Charge Mixture
The correct selection of proportioning composition is an important technological condition for the preparation of melting and casting products with the highest mullite content and less corundum and glass phasor. The aluminum-silicon coefficient (Al2O3/SiO2 mass ratio) of the batching characterized the relative content of Al2O3 and SiO2 in the batching. Theoretically, the aluminum-silicon coefficient (2.8 ≤ 2.9) of mullite solid solution should be used. However, at high temperature melting, the volatilization and reduction of SiO2 consume a part of SiO2, so that the content of Al2O3 in the ingredients is relatively increased. Therefore, in the actual batching, the actual control ratio of aluminum-silicon coefficient is lower than the theoretical value, which can generally be used. Take about 2.50.
Melt
The main equipment of melting is electric arc furnace. There are two kinds of fixed type and tilting type. In industrial production, tilting single-phase or three-phase electric arc furnace is used. Using low voltage and high current system, the general voltage is 150 V / 190 V, and the current intensity is 1600 A. The melting temperature is between 1900 ℃ and 2200 ℃.
Teeming
The molten liquid is injected into a certain shape and size model and cooled into a compact and uniform structure with a certain shape and size. Castings should have as precise a size as possible in order to minimize the amount of machining. The pouring model is made of quartz sand with high purity and mixed molding with proper amount of binder.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is generally divided into two stages: crystallization and annealing:
Crystallization. For fused-cast mullite products, it is hoped that the mullite crystal in the product is in the form of fibrous or fine crystal grains and is uniformly distributed, and the main factor to
determine the grain size is the cooling rate.
From the equilibrium phase diagram of Al2O3-SiO2 system, it can be seen that mullite is a uniformly molten compound, which is solidified and precipitated directly from the solution, and corundum is not precipitated in advance. However, when there is a certain amount of flux in the molten fluid, corundum precipitates first when the melt is cooled, while mullite crystal begins to precipitate stably below 1750 ≤ 1800 ℃. Therefore, it should be kept in the temperature range between the beginning of crystallization and 1800 ℃, and the temperature below the beginning of crystallization of mullite should be given an appropriate holding time, or sufficient slow cooling, so that the early precipitated corundum crystal can be formed by interaction with molten fluid for enough time. Mullite, so that the mullite in the product has the maximum content.
Annealing. In the cooling process of the castings after crystallization, due to the uneven heat dissipation of each part, there is a temperature gradient in the castings, resulting in great stress, which will lead to cracking or lack of edges and angles of waste products. The higher the cooling rate, the greater the tendency of waste products. Therefore, the castings must be cooled slowly.
There are two methods of annealing: self-annealing and external heating annealing. Self-annealing depends on a good thermal insulation outside the mold. Vermiculite is commonly used as thermal insulation material layer. The cooling rate can be adjusted by the thickness of the insulation. The range of slow cooling temperature is mainly 1800 ℃ 1100 ℃, which is generally controlled at 60 ℃ 70 ℃ / h. Tunnel annealing furnace is often used for external heating annealing, and the cooling rate can be controlled at less than 100 ℃ / h.
Machining
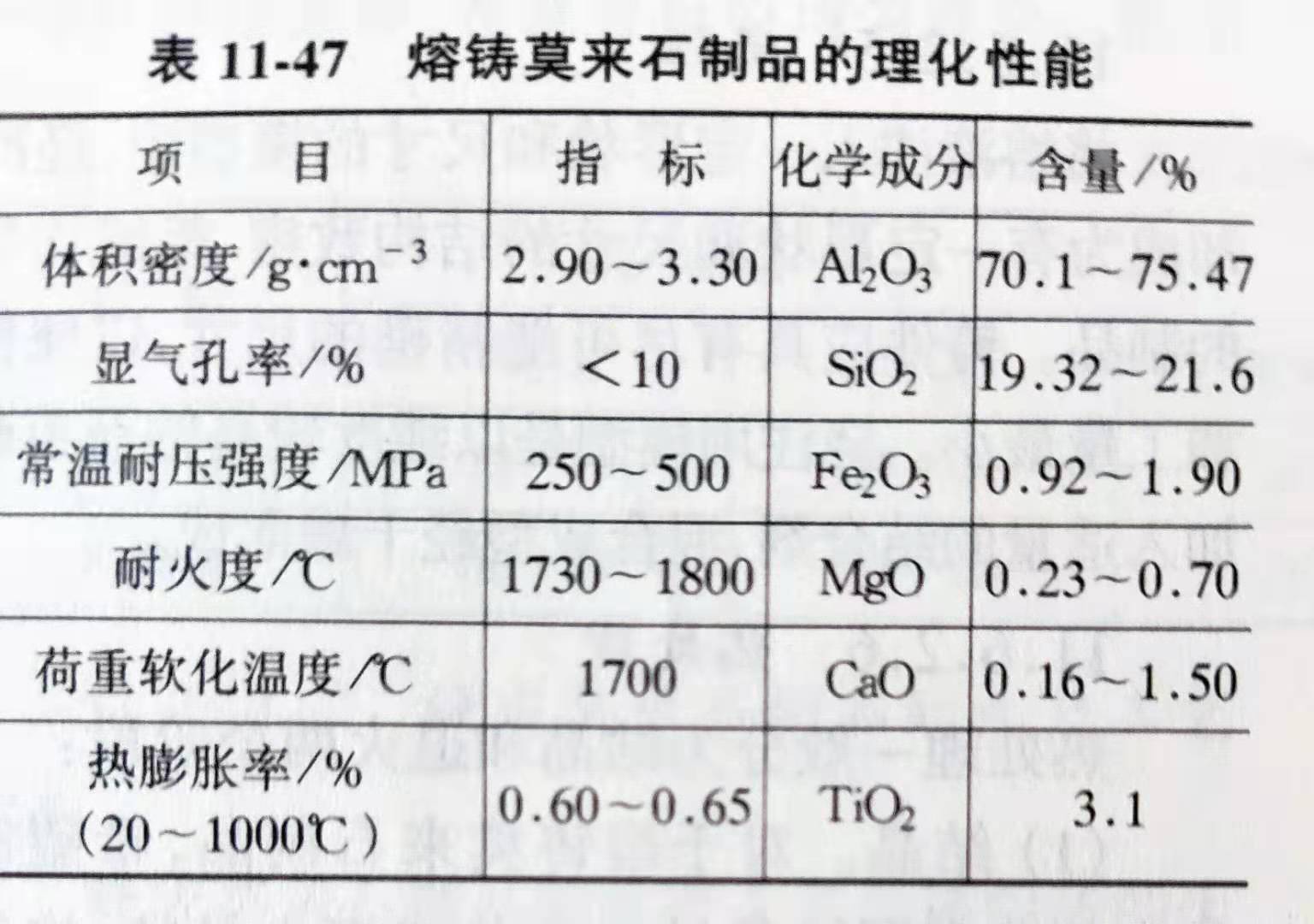
Because the shape of the model is not accurate enough, the shrinkage up and down during pouring is not consistent, resulting in shrinkage holes, as well as casting mouth and surface wrinkle, all of which need to be processed before they can be used. However, the hardness of castings is very large and it is difficult to process them. The rough diamond grinding wheel combined with phenolic resin is usually used to cut. The physical and chemical properties of molten mullite products are shown in Table 11-47.