Calcium Aluminate Cement Combined Castable
The mixture composed of refractory aggregate, binder and admixture, mixed with water (or liquid binder) into the construction of the mud available pouring method is called refractory castable. The difference with other amorphous refractories lies in that the refractory castable has a certain setting and hardening time after construction, so the pouring molding can be put into baking after a certain time of natural curing.
However, the refractory castable itself can be divided into vibrating castable and artesian castable according to its performance. The vibrating castable is a kind of thixotropic mud, which has a certain yield value. During construction, an external force (vibration force) is applied to overcome the yield stress to make the mud flow and fill the model, so it is also called thixotropic castable. And gravity pouring material is a kind of bingham body sludge yield value is very small, do not need to exert force when construction (vibration), depend on the weight and the potential energy difference can flow, and automatic packing model and automatic flat clay material, the castable for using slurry pump, through the rubber hose pump construction, thus can also be referred to as the pump irrigation castable. At the same time, this kind of castable can also be installed in the outlet of the pumping pipeline nozzle, add flash flocculant at the nozzle, spray construction, this kind of castable is also known as spray castable.
Refractory castables can be divided into heavy (dense) castables according to the volume density of the aggregate (aggregate and powder) used. The volume density is generally greater than 2.0g/cm3. Medium weight castable, volume density 1.0~2.0g/cm3; Light castable, volume density 0.4~1.0g/cm3.
According to the different properties and bonding mechanism of the binder used, it can be divided into hydration combined castable, such as calcium aluminate cement, Portland cement combined castable; Chemically bonded castables, such as phosphate, sodium, and potassium silicate bonded castables; Agglomerate combined castable, such as SiO2, Al2O3 and other powder combined castable; A hydrated - condensed castable, such as a calcium aluminate cement with SiO2 powder.
According to the chemical composition and properties of the aggregate used, can be divided into clay, high aluminum, silicon, magnesium (alkaline), aluminum magnesium, magnesium chrome, magnesium zirconium, silicon carbide and other castable. According to the main crystalline phase composition of the aggregate can be divided into mullite, jade, zirconium jade, zirconium mullite and other castables and according to the oxide and non-oxide compound name named castables, such as al2o3-sic, al2o3-sic -C, steel fiber reinforced castables. However, in order to indicate the properties of the castable, it is generally named after the name of the binder used and the name of the main aggregate, such as calcium aluminate cement combined with jadeite castable, phosphate combined with high aluminum castable, etc.
The preparation process of refractory castable is relatively simple. It is to mix the aggregate and powder, binder and admixture with a certain grain size. When used, water is added to blend the clay material with a certain thixotropy or artesian property. However, the granularity composition of refractory aggregate is also different according to the requirement of operation performance. According to Andreassen's particle size distribution equation (CPFT/100=(D/DL)q), the particle size distribution coefficient q of vibrating castable can be larger, generally q=0.26~0.35. The q value of the artesian castable should be between 0.21 and 0.26. This is because the vibrating castable is caused by external forces to produce a tight accumulation of aggregate particles in the castable, and the particle gap after the accumulation is filled by the matrix (powder and water suspension). Therefore, the q value can be larger, that is, the proportion of aggregate can be more appropriate. The artesian pouring material is based on the action of the artesian potential difference of the matrix to produce the flow and fill the model. The aggregate is buried in the matrix and dragged by the matrix to produce the flow. In general, the particle size composition of artesian materials is greater than 1mm35%~40%, 1~0.045mm15%~30%, and less than 0.045mm35%~40%.
Calcium aluminate cement is used as the binder and the castable mixture is made up of the refractory aggregate and the admixture with a certain granule grade. The mixture can be put into direct use after mixing with water, vibrating pouring molding (or artesian molding), curing and baking. This kind of material can be directly poured on the industrial furnace into the integral lining, or can be prefabricated into the block masonry used in the industrial furnace. Calcium aluminate cement with different purity and grade and refractory aggregate can be used to prepare this kind of castable according to the working conditions of industrial furnaces.
There are two types of calcium aluminate cement used in the preparation of calcium aluminate cement combined castable: one type is ordinary calcium aluminate cement, which is made of natural high-alumina and limestone raw materials, in a certain proportion, by grinding, pelleting and calcination. Its chemical composition is w (Al2O3) 53%~66%,w (CaO) 24%~37%; The other is pure calcium aluminate cement, which is made by calcining or electromelting with industrial alumina and limestone as raw materials in a certain proportion. Its chemical composition is w (Al2O3) 71%~80%, w (CaO) 18%~26%. The chemical composition and phase composition of these two types of calcium aluminate cement are shown in table 17-1. Table 17-2 shows the label number and physical properties of ordinary calcium aluminate cement.
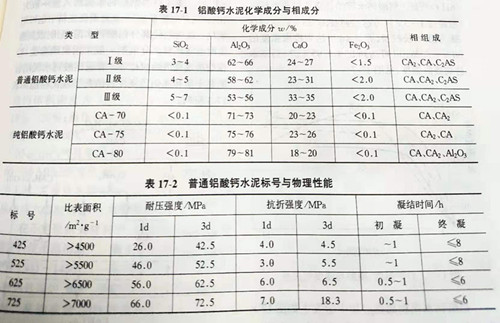
The hydration of calcium aluminate cement varies with the curing temperature. When curing below 21℃, the hydration generated is mainly CaO·Al2O3·10H2O(CAH10) and aluminum glue (AH3); between 21℃ and 35℃, it is mainly 2CaO·Al2O3·8H2O(C2AH8) and aluminum glue (AH3); when curing above 35℃, it is mainly generated 3CaO·Al2O3·6H2O(C3AH6) and aluminum glue (AH3), and its reaction is as follows:
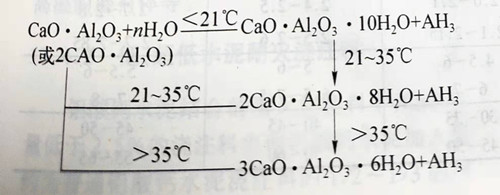
At room temperature, only C3AH6 is stable hydrates, while CAH10 and C2AH8 are both metastable hydrates. With the extension of time or the increase of temperature, they are converted to C3AH6, which causes the strength of the bonded castable to decrease. The reasons are:
(1) CAH10 and C2AH8 are six-principle or flake hydrates, while C3AH6 is cubic granular hydrates. The binding strength of C3AH6 is not as strong as that of CAH10 and C2AH8.
(2) the true density g/cm3 of CAH10, C2AH8 and C3AH6 is 1.72/1.95 and 2.53, respectively. Therefore, when CAH10 and C2AH8 are converted into C3AH6, the void fraction in the cement phase increases, and the binding area of the cement decreases, resulting in a decrease in strength.
(3) when the alumina gel (Al2O3,aq) is converted into the crystalline phase, the true density will increase, the void ratio of the bonded castable will increase, and the bonding strength will decrease.
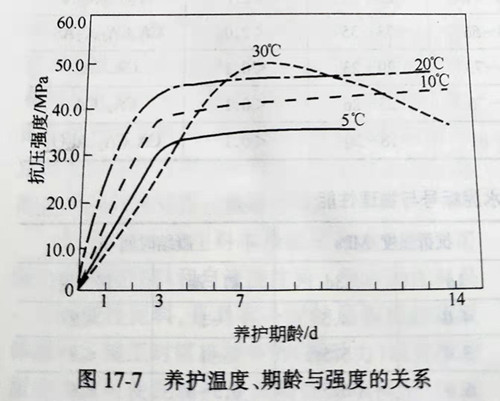
The effect of curing temperature on the strength of the castable bound by calcium aluminate cement is shown in figure 17-7. Usually at about 20℃ curing can obtain a higher strength, less than this temperature hydration is not complete, strength is difficult to reach the highest value, higher than this temperature (such as 30℃), after reaching the highest value will appear strength regression phenomenon, the reason is that the initial generation of hydration CaO·Al2O3·10H2O or 2CaO·Al2O3·8H2O will gradually convert into 3CaO·Al2O3·6H2O caused by. After the forming of calcium aluminate cement combined castable, the initial setting can be achieved after 1~3h, and the final setting can be achieved after 6~8h. The strength increases rapidly. After 1d of curing, 60%~80% of the ultimate strength can be achieved; after 3d, 85%~95% can be achieved; after 7d, the ultimate strength can be basically reached, as shown in figure 17-7.
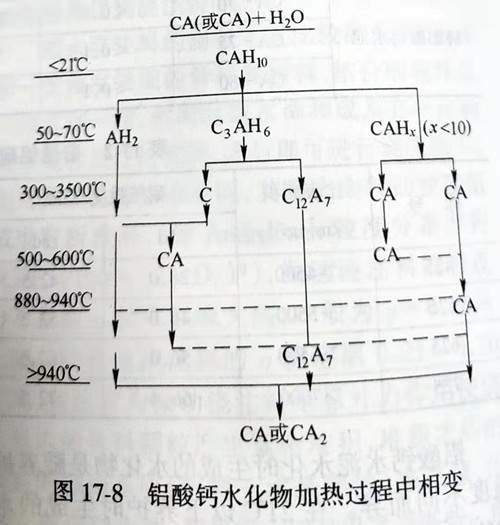
Calcium aluminate hydrates will happen in the heating process as shown in figure 17-8 of the phase change, which will happen hydrates and make the hydration key damage, dehydration and decomposition at the same time by low density of natural gas hydrates into a new phase in high density, molar volume shrinking, void fraction increases, so after heating temperature in the treatment of calcium aluminate cement castable strength of significant decline. Only when the material substrate is sintered when heated to a high temperature of more than 1250℃ and ceramic bonding occurs, will the strength of the cold state be increased again.
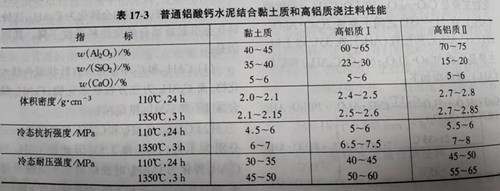
When preparing castable with clay and high aluminum refractory aggregate, ordinary calcium aluminate cement is generally used as binder, while when preparing castable with mullite and jade refractory aggregate, pure calcium aluminate cement is generally used as binder. The particle size composition of the castable can be determined by Andreassen equation, and the particle size distribution coefficient q=0.26~0.35. The amount of calcium aluminate cement added to the castable is generally 10%~15% (mass ratio). Silicon oxide powder can also be used to replace part of calcium aluminate cement in this kind of castable to prepare high strength and wear resistant castable. Dispersants are generally polyphosphate, citrate or polyacrylate. Typical physical and chemical properties of common calcium aluminate cement bonded clay and high aluminum castable are listed in table 17-3.

When pure calcium aluminate cement is used as binder, sintered or electrofused corundum is generally used as aggregate. This kind of castable particle size composition and the content of cement with ordinary calcium aluminate cement castable is similar, but choose the pure calcium aluminate cement according to the conditions of use to determine the grade, most commonly the CA - 70 level or CA - 75 level cement, because the two levels of fast setting of cement phase CA and slow setting phase CA2 proportion of moderate, setting and hardening of the appropriate speed, performance is stable. The castable made of rigid jade by using ca-70 grade cement as binder has a compressive strength of 40~50MPa after 3d curing at room temperature. The volume density after baking at 110℃ for 24 hours is 3.0-3.2g /cm3. The porosity is 18%~20%. The compressive strength is 60~80MPa; The line change rate is 0%; At 1500℃, the volume density after 3h burning is 2.9~3.05g/cm3. The porosity is 17%~19%. The compressive strength is 60~80MPa; The linear change rate is +0.5%, and the linear change rate is positive, which is mainly caused by the reaction of CaO in cement and the matrix Al2O3 to produce calcium hexaaluminate, resulting in micro-expansion.
Among amorphous refractories, calcium aluminate cement is the most widely used castable. The use temperature of clay castable is 1300~1450℃. It is generally used as the lining of steel rolling heating furnace, various heat treatment furnace, boiler, shaft kiln and rotary kiln. The use temperature of high aluminum castable is 1400~1550℃, which can be used as the lining and burner of various heat treatment furnace, steel outlet of electric furnace, high temperature section of lime shaft kiln, kiln head of rotary kiln, boiler of power plant, etc. The castable is mainly used as the lining of various high-temperature furnaces and components, such as the lining of the impregnating tube of the liquid steel vacuum degasification device, the lining of the jet metallurgy and argon blowing integral spray gun, the lining of the triangle of the top of the electric furnace, the LF furnace cover, the lining of the high-temperature wear resistance of the catalytic cracking reactor in the petrochemical industry, etc.

