Zircon Refractory Ramming Material
High aluminum - silicon carbide - carbon ramming material
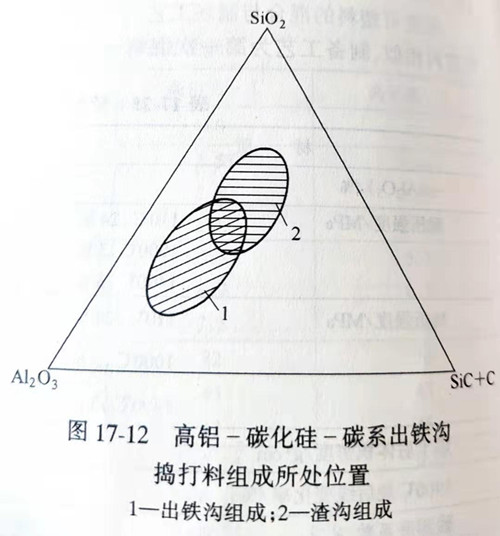
By high aluminum clinker, silicon carbide, carbon materials, binders and additives composed of ramming construction mix, known as high aluminum - silicon carbide - carbon ramming material. This kind of ramming material is mainly used for the lining of blast furnace ditches and slag ditches. See fig.17-12 for the chemical composition of the ramping materials in the outlet ditch and slag ditch. The main components of the outlet ditch are Al2O345%~69%,SiC+C 10%~25%, Al2O335%~45%, and SiC+C 15%~30%.
The preparation of high alumina clinker of this kind of grinding material requires the lower the content of impurities (Fe2O3,R2O), the better, the water absorption rate is less than 4.5%, its particle size composition is coarse particles (8~2mm) 40%~60%, medium particles (2~0.074mm) 10%~20%, fine particles (less than 0.074mm) 30%~40%. Carbon materials can be used metallurgical coke or graphite, requires low impurity content, fixed carbon content is high. Soft clay or bentonite can also be added to improve the performance of ramming materials and sintering in use. According to the use of different temperatures can also be added under different temperatures of sintering agent.
Such ramming materials used in the binder asphalt, tar (anthracene oil) + asphalt, liquid phenolic resin, aluminum phosphate, etc. When using asphalt as binder, mixing ramming materials need to be mixed with water, ramming after use before baking. When using tar (or anthracene oil) + asphalt as binder, mixing ramming materials do not need to add water, ramming without baking can be directly connected to the molten iron, in order to avoid baking ramming materials, but the use of flue gas is larger, will pollute the environment. When using liquid phenolic resin as binder, there is no need to add water, no need to bake directly put into use, also belong to free from baking ramming materials, light pollution to the environment, but ramming materials storage period is short, it is best to use directly field deployment. When aluminum dihydrogen phosphate is used as binder, the corrosion resistance of molten iron and slag is poor, so it can only be used as the lining of small blast furnace outlet ditch. Now basically aluminum dihydrogen phosphate is not used as binder.
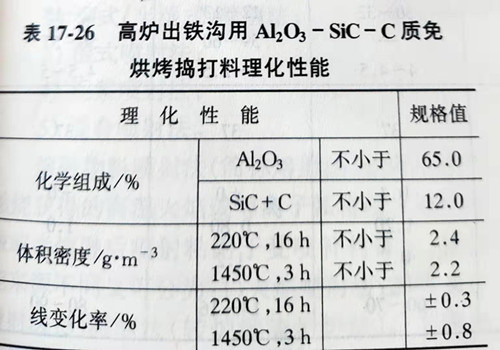
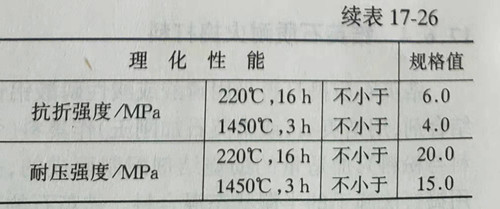
Additives used to improve the properties of high aluminum - silicon carbide - carbon ramming materials include antioxidant, plasticizer, wetting agent, anti - shrinkage agent, etc. The purpose of adding antioxidant is to prevent the excessive oxidation of carbon materials, usually using metal silicon powder, metal aluminum powder as antioxidant. Plasticizers generally use plastic clay. The purpose of adding the wetting agent is to make the silicon carbide and carbon materials mix well with the oxide refractories. In order to prevent the use of the anti - shrinkage agent to shrink too much and make the groove lining crack, generally can be used as anti - shrinkage agent silica particles. Table 17-26 shows the properties of baking free al2o3-sic -C ramming of phenolic resin. At present, the high aluminum - silicon carbide - carbon ramming materials used in the outlet of medium and small blast furnaces have been gradually transferred from the type that needs to be baked to the type that does not need to be baked. The advantage of non-baking ramming material is that it can save the time of repairing the groove, and can also avoid the excessive oxidation of carbon material in the baking process, so that the groove lining of slag permeability and erosion resistance to reduce.
Alkaline refractory ramming compound
The basic refractory ramming material is a mixture of sintered or electro-fused magnesia (or magnesium-calcium sand, magnesium-calcium iron), binder and admixture (sintering agent) which can be rammed in semi-wet state. Alkaline refractory ramming ramming materials have water alkaline ramming ramming materials and non - water alkaline ramming ramming materials. Water-containing alkaline refractory ramming materials cannot be directly mixed with water, because water will react with MgO to form Mg (oh) 2, resulting in bursting or fragmentation of ramming linings. Therefore, it is necessary to use binders that can prevent magnesia from hydration into Mg (oh) 2. Such binders include magnesium chloride (brine MgCl2·6H2O) aqueous solution, magnesium sulfate aqueous solution, water glass and polyphosphate aqueous solution, etc., which can react with MgO to form complex salt (or complex salt) and produce binding effect.
In the past, water-containing alkaline refractory ramming materials were mainly made by brine, mainly used to construct or repair electric furnace and open hearth furnace melting pool and steel trough. Nowadays, polyphosphate solution has been gradually used as binder, which can prevent magnesia hydration more effectively, but at a higher cost.
Anhydrous alkaline refractory ramming material is dehydrated tar and asphalt, or liquid phenolic resin as a binder. The ingredients are magnesia (or magnesium-calcium sand) 86%~90%, sintering agent (iron oxide powder or magnesium-calcium iron sand) 2%~3%, asphalt powder or graphite powder 3%~7%, plus dehydrated tar or liquid phenolic resin 9%~11%. The particle size composition of batching is generally 3.5~1.5mm,40%; 1.5 ~ 0.5 mm, 20%; Less than 0.5 mm, 40%. Using wet mill mixing. Such ramming materials can be used as bottom and slope lining materials and repair materials for electric furnaces, and can also be used as filling ramming materials between magnesia bricks and permanent linings for converter furnaces.
Zircon refractory ramming material
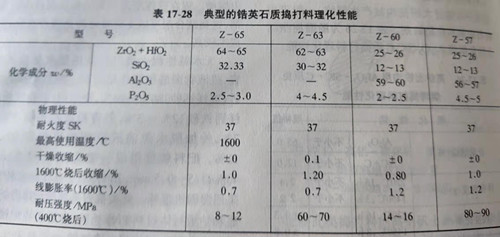
Zircon stone ramming material is made of phosphoric acid or acid aluminum phosphate as the binder, zircon (or zircon and corundum) as the aggregate (aggregate and powder), plus appropriate amount of combustion aid preparation, ramming construction of semi-wet state mixture. The theoretical chemical composition of zirconium is: ZrO2 67.2%,SiO2 32.6%. The zirconium used as ramming material requires ZrO2 content not less than 63%. Zircon is decomposed into monocline ZrO2 and amorphous SiO2 during high temperature heating. The decomposition temperature of zircon is greatly affected by the content of impurities. The decomposition temperature ranges from 1540℃ to 2000℃.
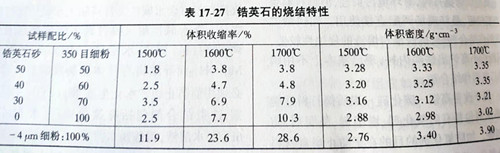
Zircon sintering is carried out by solid phase diffusion under high temperature, its speed is very slow, it is difficult to fully sintering, adding some oxides can promote sintering. The results showed that the oxides promoting zircon sintering at 1500℃ were Na2O, K2O, MgO, CaO, ZnO, B2O3, MnO, Fe2O3, Co2O3 and NiO. However, it must be noted that some oxides can significantly promote zircon decomposition, and a large amount of zircon decomposition can lead to the deterioration of the ramming material's volume stability, so it is necessary to select the appropriate sintering agent and the amount added through the test. The sintering property of zircon is very important to the preparation of ramming materials. Table 17-27 shows the volume shrinkage and volume density of zircon samples of different fineness after 3h heat preservation at different temperatures. Obviously, the volume shrinkage of the sample increased with the higher the content of 350 mesh fine powder and the higher the roasting temperature. Therefore, for ramming materials, particle size composition must be considered reasonable, not only to ensure a good sintering, and do not appear too large shrinkage.
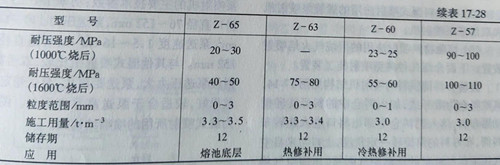
When phosphoric acid or aluminum dihydrogen phosphate is used as the binder of zirconite tamping materials, the density of phosphoric acid or phosphate solution can vary according to the requirements of the bonding strength, generally in 1.25~1.52g/cm3, the amount of addition is 6%~8%. The physical and chemical properties of typical zircon ramming materials are shown in table 17-28.
Zircon ramming material is mainly used for bottom lining of zirconium corundum mullite brick in glass kiln melting pool, filling of expansion joints of silicon brick, transition layer material between silicon and high aluminum refractory products, and lining of some induction furnaces and melt flow channels. Zirconium - bearing stone ramming materials have also been used for ladle lining, but due to high cost and limited resources, they are no longer used.