Metal Ceramic Products
Cermet: a composite material consisting of a combination of metals and various ceramic phases is called cermet. American standard method (ASTM) ceramic - metal composite materials research committee for ceramic - metal composite material is defined as: "a by a metal or alloy with the same or more ceramic phase composition of the heterogeneous composite material, which accounted for about 15% ~ 85% of the volume of material, at the same time in the preparation of temperature, the solubility of metal and ceramic facies is extremely weak."
Cermet should have both ceramic and metal excellent properties, can be made of heat, wear, corrosion resistant products, as well as products with special electrical properties. The main types of cermet are (1) metal-oxide cermet;
(2) metallized ceramics with metal-carbides.
(3) metallized ceramics with metal-nitride;
(4) metal-boride cermet;
(5) metallized - silicified cermet.
Metal ceramic with raw materials, metal ceramic requirements between the metal and ceramic phase of the ingredients to have good wetting property, because the metal ceramic belongs to liquid phase sintered composite material, so in the sintering process requirements, metal material not only for ceramic phase has good wettability, and can form the network structure of the metal, so that we can improve the structure and various properties of metal ceramic.
It is also very important to match the properties of metal raw materials and ceramic raw materials, for example, the two raw materials should not produce intense chemical reactions, nor produce low-temperature eutectic matter and low-temperature crystallization. At the same time, the linear expansion coefficient of the two materials should be as close as possible, because this is also a key problem affecting the supply performance of cermet.
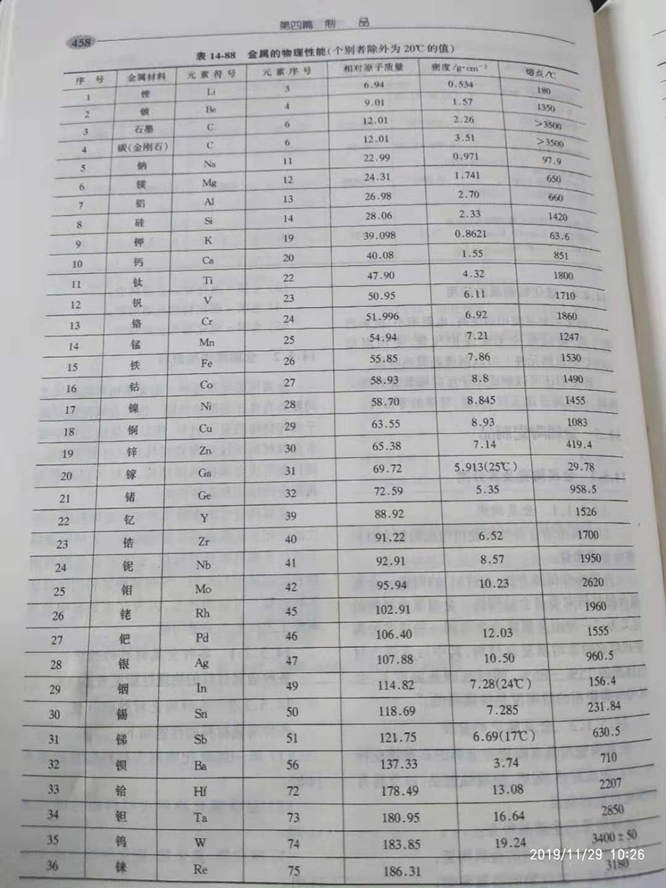
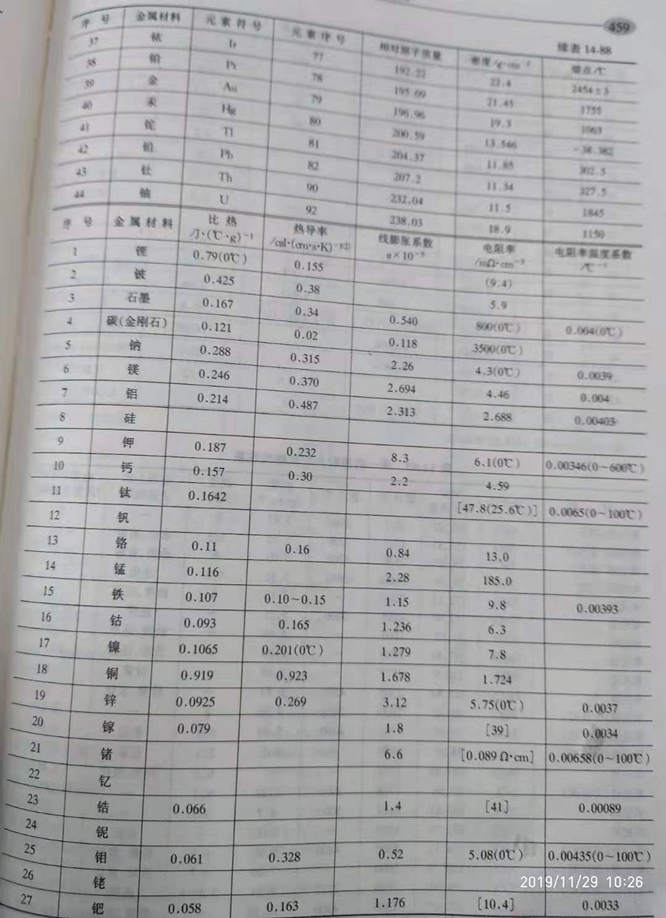
Physical properties of various metal materials are shown in table 14-88.
The properties of various ceramic materials are as follows.
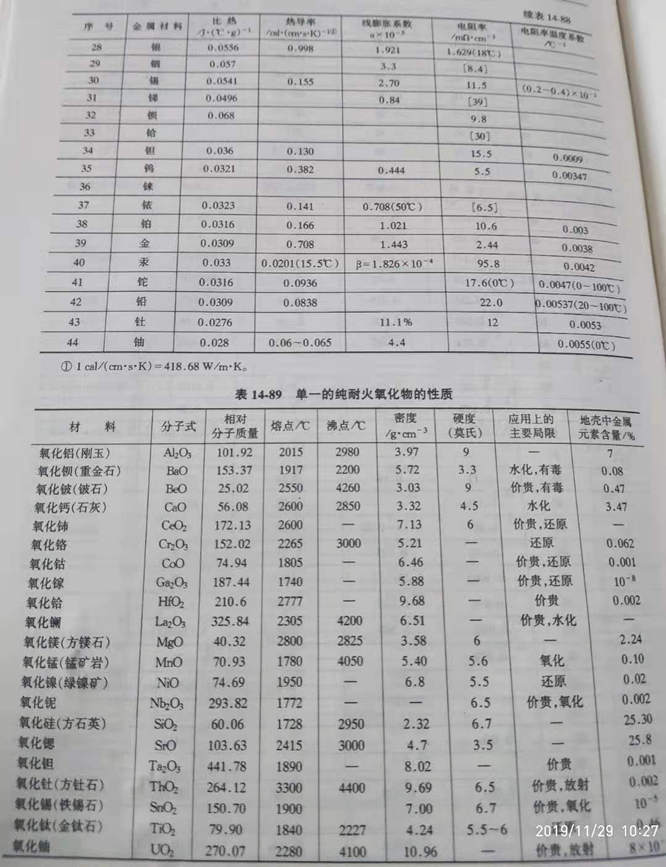
(1) the properties of single pure oxide refractories are shown in table 14-89.
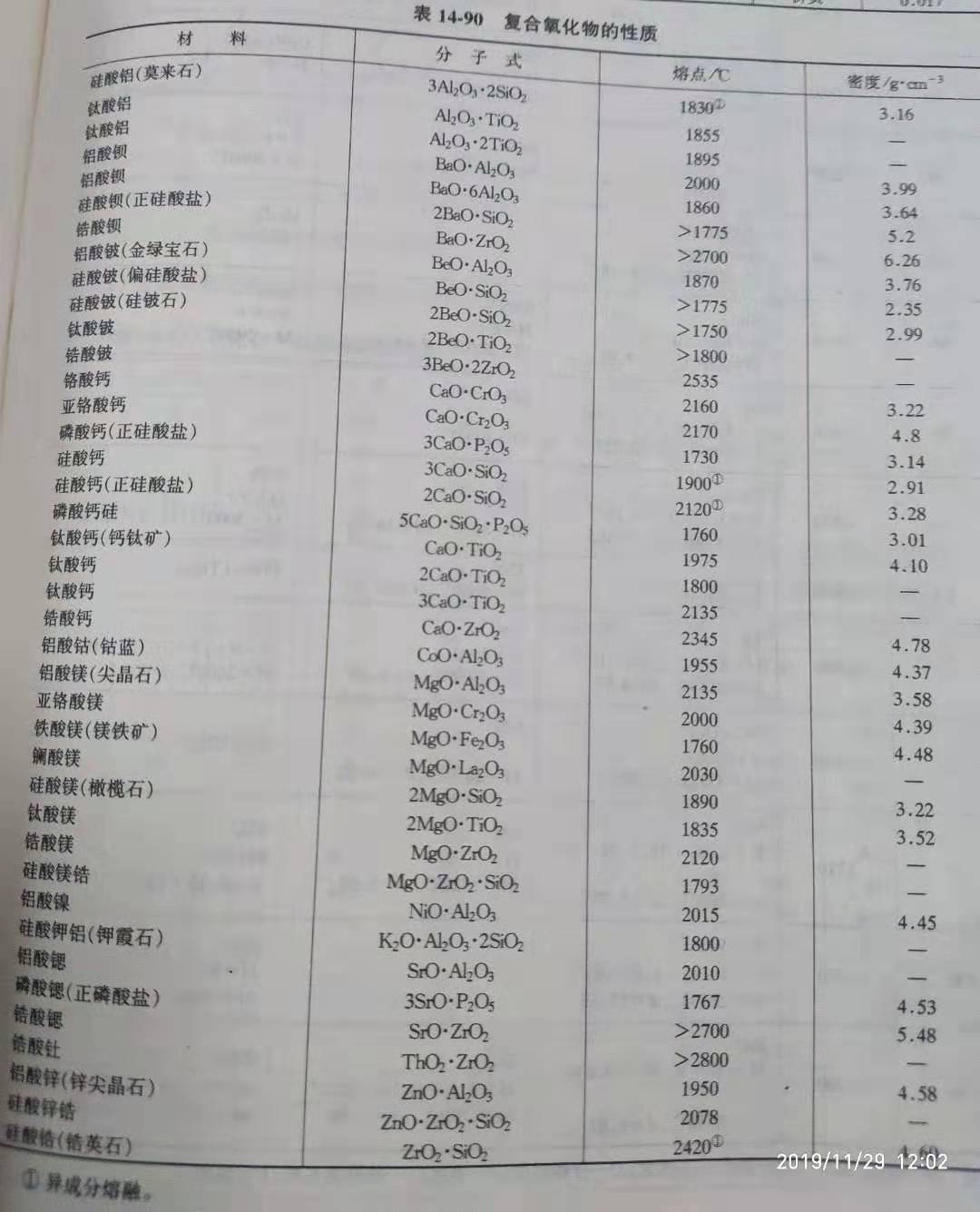
(2) the properties of composite oxide refractories are shown in table 14-90.
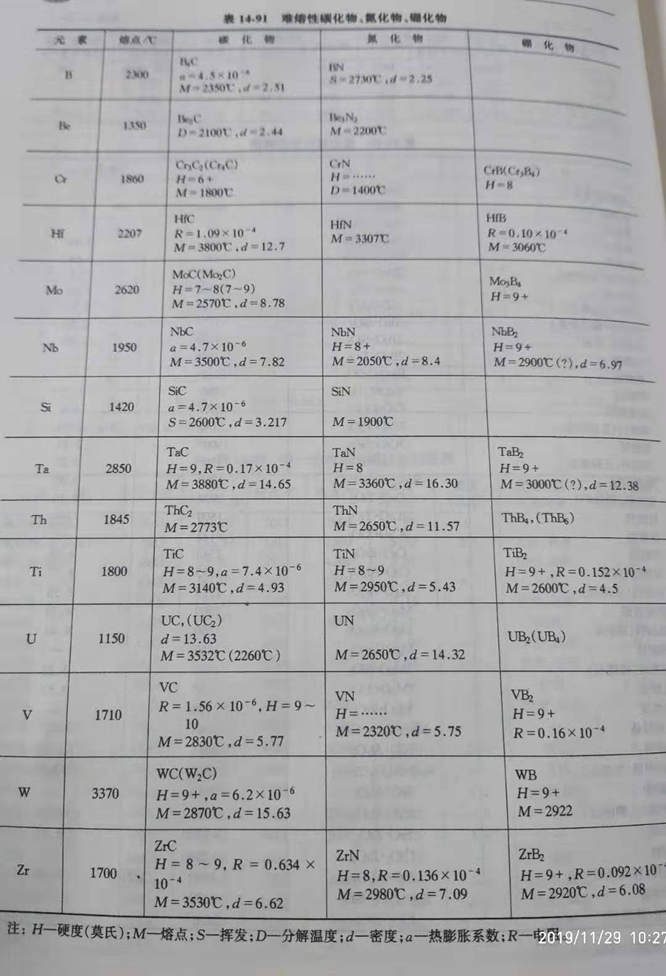
(3) the properties of carbides, nitrides and borides are shown in table 14-91.
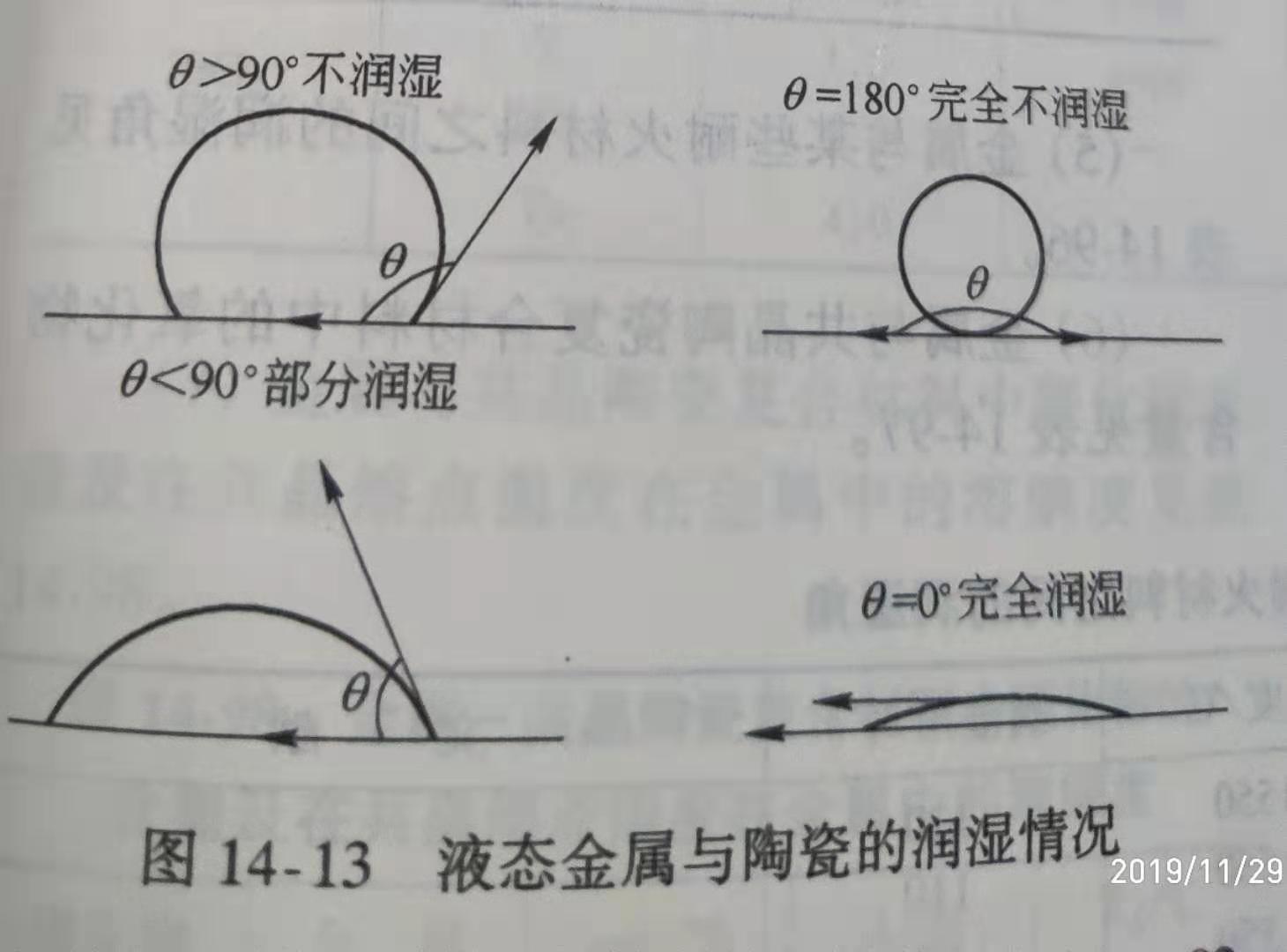
Wetting Angle between metallic materials and ceramic materials: the wettability of high-temperature liquid metal to ceramic materials is a crucial property of cermet. The wetting Angle is represented by the wetting Angle. The wetting Angle of liquid metal and ceramic materials is shown in figure 14-13.
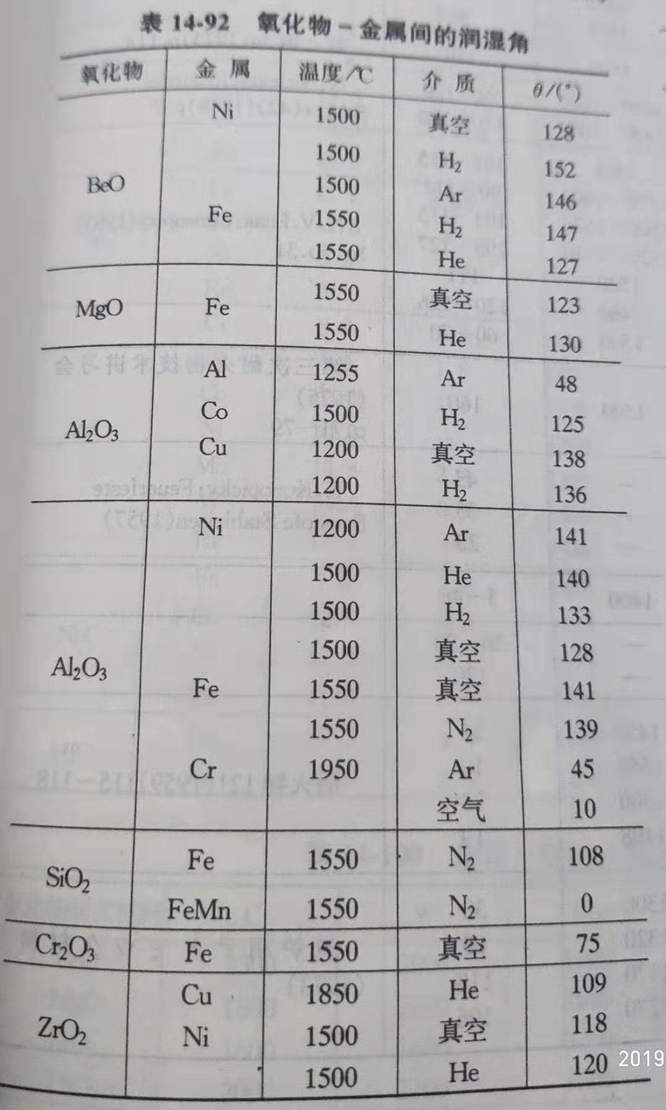
(1) the wetting Angle between metal and oxide is shown in table 14-92.
(2) the wetting Angle between metal and carbide is shown in table 14-93.
(3) the wetting Angle between metal and nitride is shown in table 14-94.
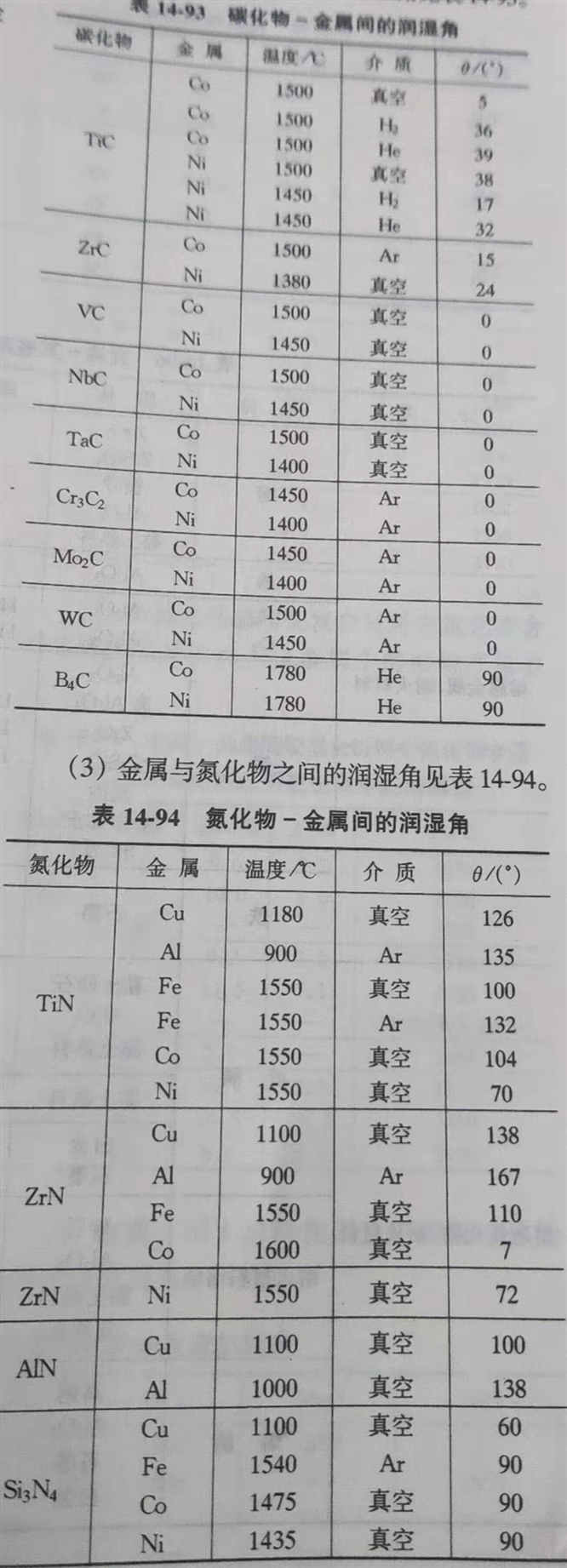
(4) the wetting Angle between metal and boride is shown in table 14-95.
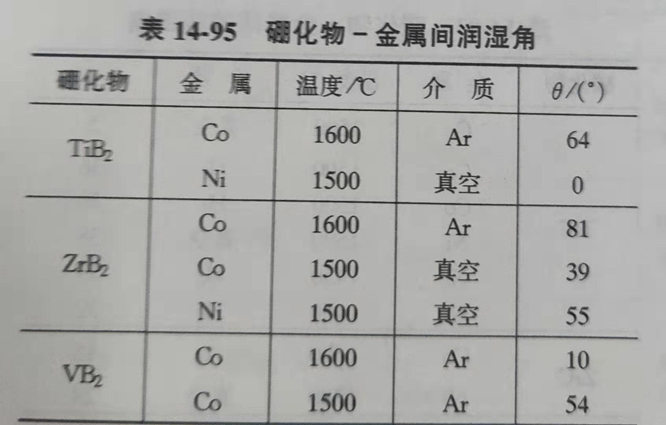
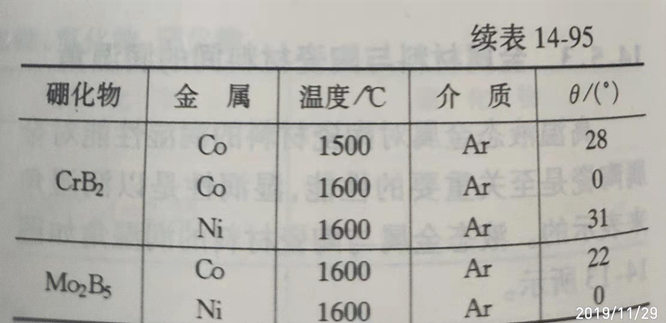
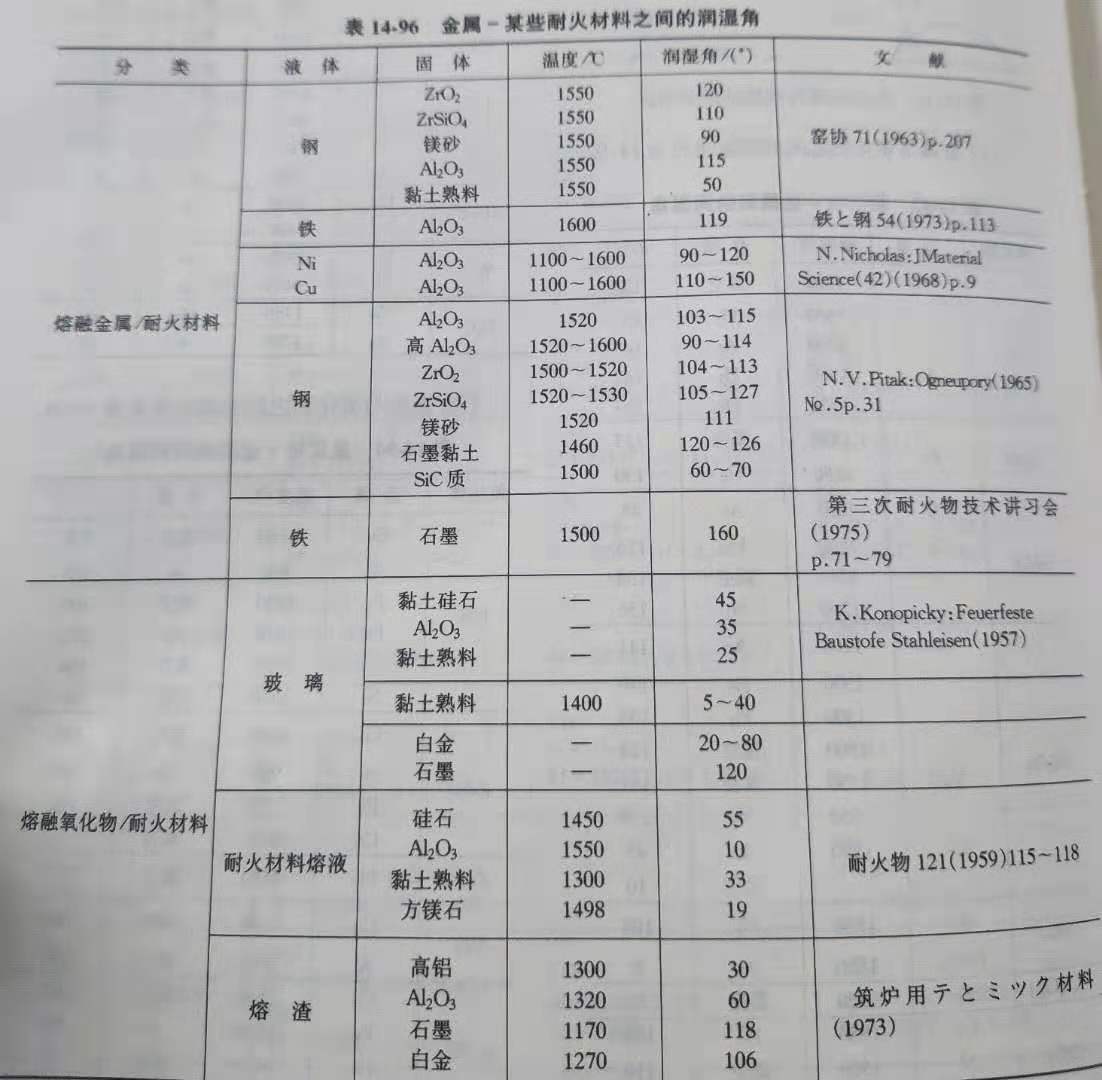
(5). The wetting Angle between metal and some refractories is shown in table 14-96.
(6). The oxide content of metal and eutectic ceramic composites is shown in table 14-97.
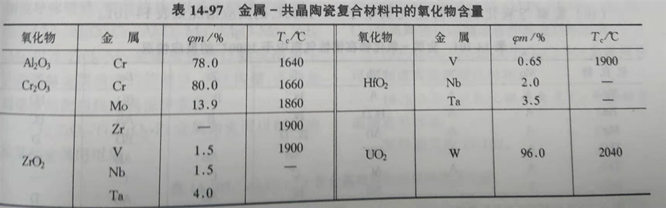
(7) the carbide content in the metal and eutectic ceramic composites and the solubility in the metal at the eutectic melting point temperature are shown in table 14-98.
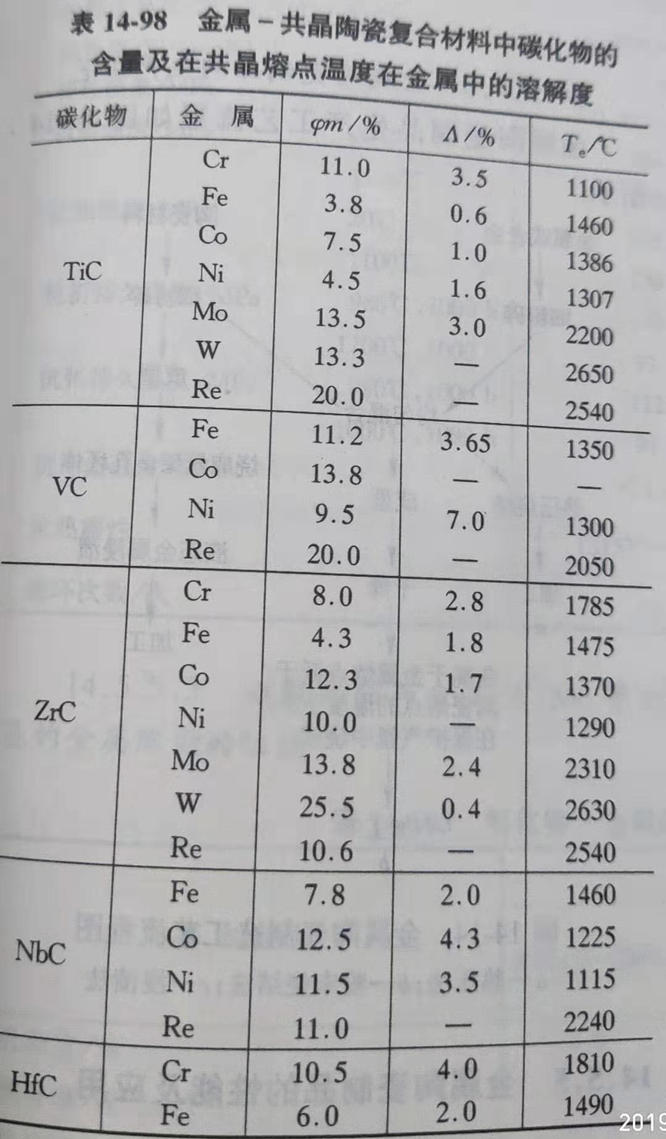
(8) nitride contents in metal and eutectic ceramic composites and their solubility in metals at the eutectic melting point are shown in table 14-99.
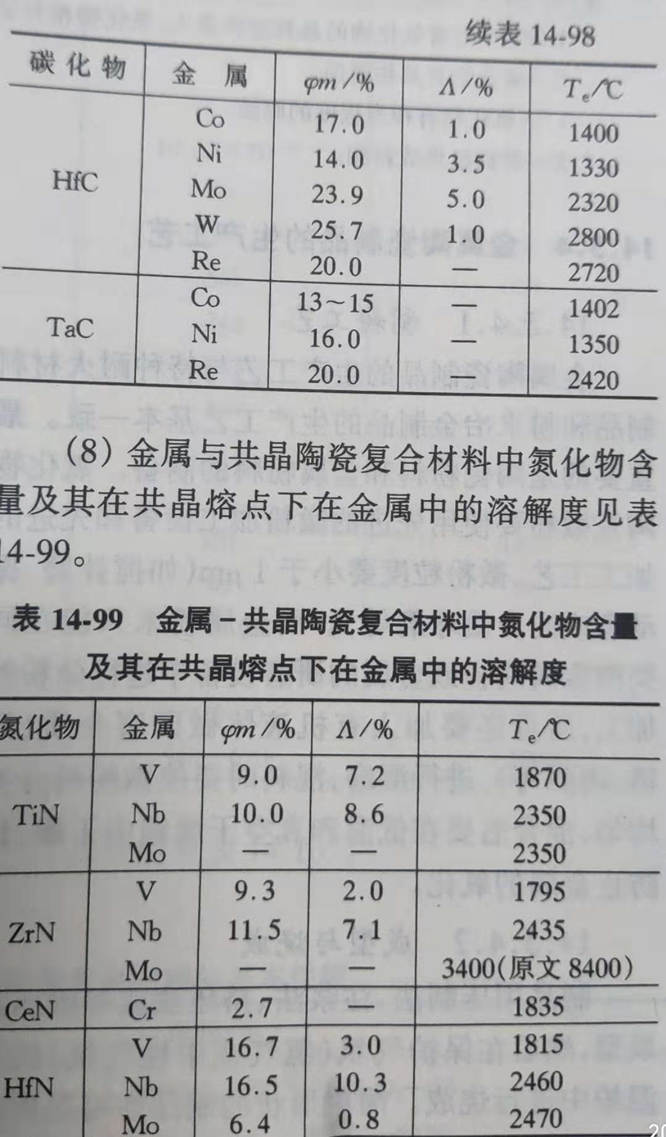
(9) the temperature at which the metal-refractory begins to react when contacted in vacuum is shown in table 14-100.
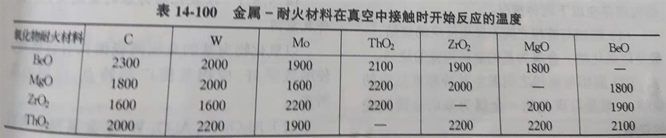
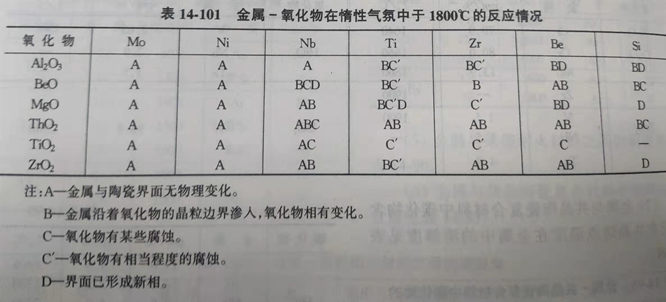
(10) the reaction of metal and oxide at 1800℃ in an inert atmosphere is shown in table 14-101.