Mechanism of Skateboard Damage
Skateboard in use often see the form of damage: skateboard surface rough (surface damage), hole edge damage, crack and peeling, cast hole expansion. The statistical proportions were as follows: crack and spalling accounted for 10%~20%, cast hole enlargement for 20%~40%, and surface roughness for 40%~60%. The factors directly related to these failures are the quality of the slide and the harsh conditions of use: the strong thermal shock at the beginning of steel pouring, chemical erosion and erosion of molten steel and slag during the process of steel pouring, thermal mechanical wear, etc. At the beginning of pouring steel, cold slide contact with high temperature molten steel, extremely strong thermal shock, hole edge easily produce crack, crack, crack. Therefore, high thermal impact resistance is the first to ensure the performance, the corresponding slide materials should have low linear expansion coefficient, low elastic modulus, high thermal conductivity, high fracture work related to this performance.
Under high temperature, strong scour of molten steel, slag and gas and thermochemical erosion are the main reasons for the failure of slide. The skateboard reacts with the high temperature steel and the air leakage through the sliding surface during use, resulting in structural loosening and damage of the skateboard. These reactions include the oxidation of carbon, [Ca], [Mn], [Fe] and other erosion of the skateboard, and the decomposition of zirconium mullite.
The oxidation of carbon plays a very important role in the thermal chemical damage process. On the other hand, the porosity of the slide is low (less than 10%), the pore diameter is small (less than 6 m), and the permeability of slag and molten steel is difficult. However, once oxidized and decarburized, the pore diameter increases by 2~5 times, and the permeability of slag and molten steel becomes possible under hydrostatic pressure. After the condensation of the permeable slag and molten steel, the lubrication of the sliding surface becomes poor, the friction increases when the slide is opened, and the spalling and roughness increase, which affects the service life. The analysis of slide plate after use shows that when the oxygen content in molten steel is greater than 90× 10-4%, the effect of graphite oxidation is obvious.
Alloy elements, oxide impurities and deoxidizer in molten steel react with refractories, which is another important reason for plate reaming and face erosion. Mn, MnO, FeO and CaO in molten steel have strong erosive effects on refractory materials, and these components are easy to react with SiO2 in the slide plate to produce corrosion, and the high temperature of molten steel will accelerate the reaction. The influence of high aluminum skateboards was significantly higher than that of aluminum carbon skateboards, and the erosion was significantly intensified when the content of manganese in molten steel was high. The analysis of aluminum zirconium carbon skateboards (Al2I3 71.5%, F.C 8.49%, ZrO2 6.23%, SiO2 6.11%) after pouring several different types of steel (calcium treated steel, aluminum killed steel, aluminum silicon killed steel) showed that: The carbon oxidizes and disappears within a certain distance from the working face, and the zirconium mullite decomposes, both of which lead to loose structure and molten steel infiltration, and react with the refractory to produce MnO·SiO2, MnO·Al2O3,2FeO·SiO2,FeO·Al2O3, [Ca] →CaO+Si,Al→ al2o3-cao and al2o3-cao -- SiO2 series compounds.
When pouring ordinary steel in baosteel, the expanding speed of aluminum zirconium carbon slide is 1~1.5mm/ furnace, and the casting speed of calcium treated steel is up to 15mm/ furnace. After pouring 1~2 furnaces, the tundish slide plate is leaking steel. In addition, oxygen blowing caused by erosion will also make the slide diameter, control loss steady. Low SiO2 content, low porosity, micro porosity and appropriate carbon content will help improve the anti-damage ability of skateboard.
From the perspective of use, the requirements of the skateboard is safe and reliable, long life, to meet the requirements of different types of steel, different steelmaking process. Based on the understanding of the damage mechanism of skateboard, the premise to improve the service life and use reliability is to improve the three properties of skateboard materials: thermal shock resistance, high temperature wear resistance and corrosion resistance; Material selection tends to be diversified; Optimize skateboard structure and application of assistive technology.
In the improvement of ladle skateboards (all fired skateboards), some examples of optimization are as follows:
(1) optimization of skateboard aperture. A smaller aperture is beneficial to increase the opening degree of the skateboard and reduce erosion, but too small will reduce the casting speed and reduce the output and quality. Generally speaking, the aperture of the block slide is 80mm, which corresponds to the maximum flow rate of 8.0t/min, which is changed to 75mm, which corresponds to the maximum flow rate of 6.4t/min, increasing the life by 14%.
(2) the board shape optimization, using FEM (finite element method) under the condition of the use of skateboard do stress analysis and strain measurement, according to the stress distribution on the skateboard appearance structure improvements, can reduce internal stress and strain, significantly reduced along the sliding direction of cracking, ladle slide life expectancy increase 2 times, tundish skateboard life increased by 30% ~ 40%.
(3) refractory optimization. The measures adopted are: adding low expansion coefficient raw materials, using alumina ultrafine powder, reducing carbon content, reducing zirconia content, reducing silica content, special additives and so on.
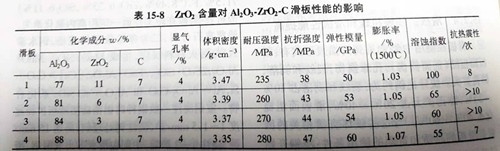
(4) the content of ZrO2 in conventional aluminum zirconium carbonized skateboards is about 10%, which has good anti-spalling property. However, when the oxygen content in steel is high, even if a small amount of FeO coexists with ZrO2, the low-melting point phase can be generated. At the same time, the excessive content of zirconium oxide will expand the microcrack when the skateboard is cooled, which limits the improvement of skateboard life. The amount of zirconium oxide in the skateboard was optimized by kurozaki, Japan. The results showed that zirconium oxide was not present and the anti-spalling property was the worst. The anti-spalling property of 3%~6%ZrO2 was good, and the specific performance parameters were shown in table 15-8.
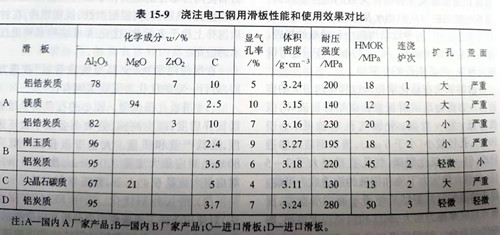
In the comparison experiment of the slide boards used for pouring electrical steel in baosteel, the diameter expanding and sliding surface wear of the slide boards with high strength and good oxidation resistance are the least. That is, aluminum carbon slide high strength, good oxidation resistance, can meet the three - furnace pouring; Aluminum zirconium carbonized skateboards have good thermal shock resistance and high strength, but due to the oxidation of carbon, the skateboard structure is loose and its strength decreases. In addition, ZrO2 easily reacts with FeO to form a low melt, which further deteriorates the structure. Magnesium slide made of high purity raw materials, high temperature burning, oil immersion, although with good corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, but low strength at high temperature, not resistant to erosion; Spinel carbonaceous skateboard USES high purity spinel and carbon black as raw materials, adding appropriate amount of antioxidants, phenolic resin combination, protective atmosphere burning, is also good corrosion resistance, high temperature strength is low, oxidation resistance is poor, not resistant to erosion; Steel jade skateboard with aluminum oxide as raw material, high temperature fired, made of oil immersion, high strength, oxidation resistance, anti - erosion, but there is a sliding area of cold steel. See table 15-9 for comparison of the performance and application effect of the slide plate used for pouring electrical steel.
The purpose of the new combined skateboard development is: from the material design to a greater extent to solve the oxidation and thermal shock resistance problems containing carbon skateboard, further improve the service life and safety of the skateboard, to meet the needs of the development and progress of steelmaking process. At present, most of them are still in the trial, improvement and improvement stage. In recent years, the metal composite base aluminum carbon skateboard with aluminum, compared with the conventional burned aluminum carbon skateboard, has better oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance. During the use of non-fired slide plate with metal aluminum, Al2O3 or/and Al4C3 will be generated, which will increase the high temperature strength and may react with FeO in slag:
3FeO+2Al (g) =Al2O3 (s) +3Fe (s).
2FeO (l) +Al2O (g) →Al2O3 (s) +2Fe (s).
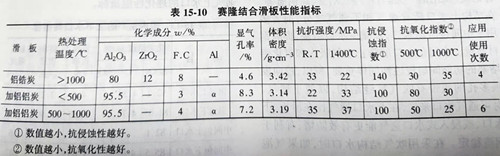
The generated Fe (s) and Al2O3 (s) play a densifying role on the working face of skateboard. The reference performance indexes of this skateboard are :Al2O3 95.8%, SiO2 4.1%,C3 1%, volume density 3.08g/cm3, apparent porosity 7.5%, normal temperature compressive strength 120MPa, normal temperature flexural strength 24MPa, high temperature flexural strength (1400℃) 32MPa. In some steel mills use the effect is far better than ordinary non - burning skateboard, also more than burning into aluminum carbon skateboard. Production features are no burning, no oil immersion, no distillation, reduce the environmental pollution, simplify the process. The skateboard with metal aluminum can be treated at 500~1000℃ to form a non-oxidized ceramic bonding phase, and then impregnated with asphalt to further optimize the performance. Table 15-10 shows the performance comparison of the aluminum-adding skateboard and the sintered aluminum-zirconium carbon skateboard.
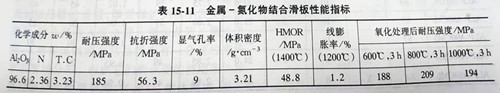
Literature [156] describes the development of non-oxide bonded (metal-nitride bonded) skateboards. Here, plate aluminum oxide is used as the main raw material, 10%~20% metal aluminum (fine powder, particles, aluminum fiber) is added, below 1100℃, a certain nitriding process is adopted to form the microstructure of metal-nitride combination phase of metal aluminum +ALN. In order to prevent ALN hydration, the skateboard was oxidized to some extent. The service life of the skateboard developed in three domestic steel mills is increased by 1 time compared with the original skateboard. Table 15-11 shows the performance indexes of metal-nitride bonding skateboards.
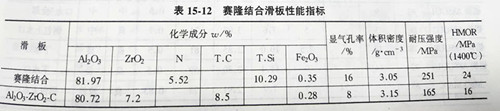
Literature [157] introduces the trial production of cylon combined corundum skateboard. The aggregate is plate-shaped corundum, and the matrix fine powder consists of plate-shaped corundum fine powder, metal silicon powder, metal aluminum powder, and -al2o3 micro powder, etc., which are formed by high pressure molding, nitriding and firing at 1450~1470℃, forming the structure of su-sialon combined with corundum phase. Performance indicators are shown in table 15-12. The pilot skateboard is used in tundish, and the erosion resistance of skateboard surface is better than that of al2o3-zro2-c skateboard.
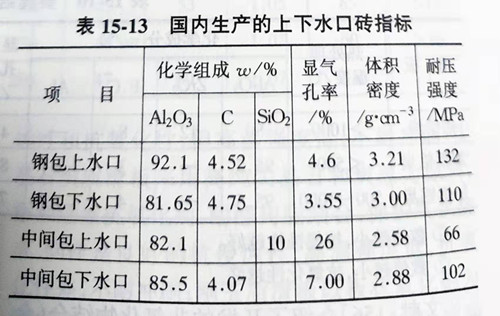
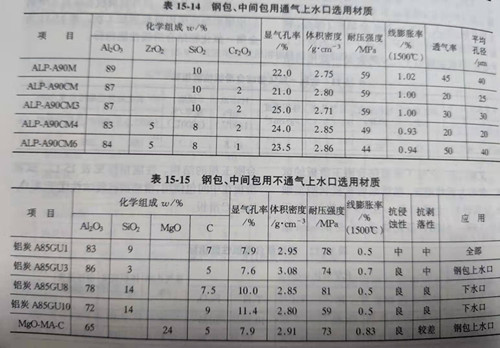
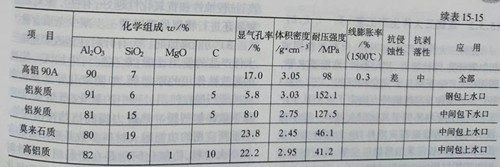
The sliding nozzle device is also composed of the upper and lower nozzle brick, which is installed in the base brick of the ladle and tundish, and the lower nozzle is installed together with the lower skateboard. In terms of performance, the water-mouth brick also needs to have similar requirements with the skateboard. Corrosion resistance under the action of molten steel and slag liquid; Wear resistance and high mechanical strength under the wear action of flowing steel; Sintering that prevents quicksand initiation has low thermal conductivity and low reactivity with quicksand initiation. The service life of ladle nozzle (upper nozzle) is usually 2~3 times that of skateboard, and it is made of aluminum carbon, alumina - spinel - carbon, corundum, high aluminum, etc. In the structure of shuikou brick ventilation and ventilation points, the former is more used in the tundish sliding shuikou, in order to reduce shuikou blockage, improve the quality of steel. The function of tunic nozzle to prevent air inhalation and blockage of alumina is as important as corrosion resistance, so porous or vented slit structures tend to be developed to facilitate ventilation. For ventilatable nozzle, ventilation at the upper nozzle is more effective in preventing blockage and stabilizing the steel flow than at the slide board, lower nozzle or immersion nozzle. When using blowing nozzle structure, if bubbles can't rise in the crystallizer, can cause porosity in the casting defects, so now the technology tend to reduce the volume, at the same time also require air bubbles will rise to liquid level, therefore, has developed an narrow pore size distribution of porous materials, there is a optimal flow configuration (back pressure order of magnitude as follows: 0.15 ~ 0.16 MPa). Recently, with the development of continuous pouring in multiple furnaces and high speed pouring, the quality, performance and reliability of ventilation nozzle are more important. The main materials are aluminum carbonaceous, mullite, high aluminum, zirconium, etc. Quartz is added to improve spalling resistance and impregnated asphalt improves corrosion resistance. Table 15-13 shows the indicators of the upper and lower shuikou bricks produced in China. Table 15-14 and table 15-15 respectively list the physical and chemical performance indicators of the ventilated upper shuikou for some intermediate packages, ladle and non-ventilated upper shuikou for intermediate packages of shinagawa company, Japan.