Compact Zircon Products and Zirconium Corundum Products
Zircon products with an apparent porosity of less than 11% are called compact zircon products. Dense zircon products of high temperature strength, strong resistance to erosion of glass liquid, widely used in glass melting kiln floor paving brick and kiln body superstructure, such as: arch corner brick, corner brick, parapet brick, transition brick, temperature measuring hole brick, observation hole brick, also suitable for melting glass glass fiber with the lining of glass pool kiln melting pool.
There are two grades of high density zs-g and zs-z. Physical and chemical properties of JC/ t495-92 (96) for dense zircon bricks for glass melting furnace are shown in table 16-3.
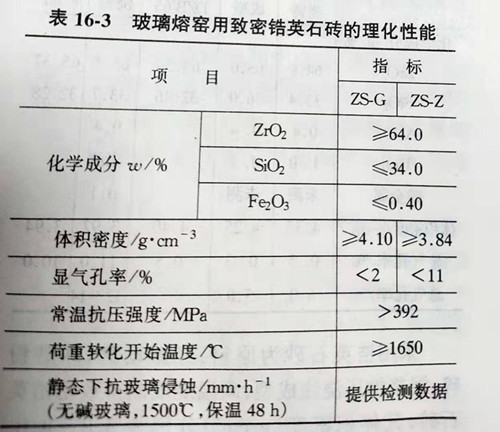
Zirconium brick with high density and low porosity is usually made of fine powder, formed by pouring or isostatic pressing and fired at high temperature.
Zircon concentrate size is generally less than 0.125mm, (e.g
, 0.125~0.088mm accounts for 14.2%, 0.088~0.066mm accounts for 24.6%, less than 0.066mm accounts for 61.2%). If the particle size distribution is appropriate, it can be directly used as the raw material for isostatic pressing, otherwise it needs to be processed by grinding, spray drying for granulation, and then used for isostatic pressing.
The biggest characteristic of isostatic pressing is that all parts of the mud are uniformly compressed and the pressure is very high, so that the density of the blank body is high and uniform, so that the deformation and contraction of the blank body in the firing process is greatly reduced, and the blank body formed by the general molding method will not be burned to crack due to the pressure generated by the density difference. In addition, isostatic pressure molding pressure operation is simple, molding pressure adjustment is convenient, molding rubber or plastic mold manufacturing is convenient, can be used repeatedly; The temporary binder can be used less or less in the mud, which is beneficial to improve the density of the blank body, high quality compact zirconium brick, usually using wet bag cooling isostatic press molding, molding pressure of 180~250MPa.
TiO2 was added as sintering agent, adding 0.5%~1.5%, TiO2+Al2O3+MgO compound additive had a better effect, and the sintering temperature of the product was 1500~1600℃. The physical and chemical properties of the compact zircon brick were shown in table 16-4.
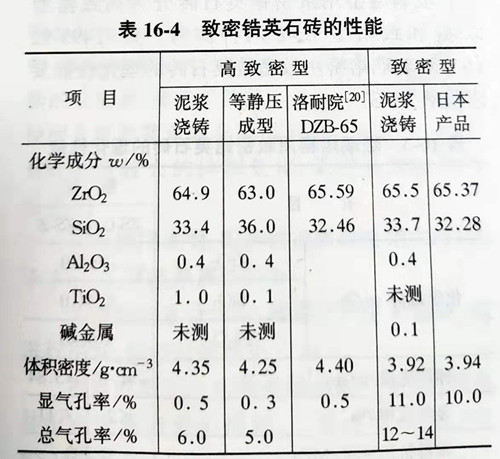
Using zircon stone sand as raw material, through vibration mill, ball mill pulverization, mud pressure pouring molding, high temperature fired to produce dense zircon brick, its volume density (g/cm3) is 3.8~4.0, 4.0~4.2, the apparent porosity (%) is 5~10, 0.5~2.0, the product has been used in many glass factories on the non-alkali ball kiln, the effect is good.
Dense zircon brick has the advantage of good glass erosion resistance, not in the formation of air bubbles in the glass, stone, such as spot defects, mainly used in the area of contact with the glass, especially the system of molten alkali content less than 5% of the glass fiber kiln and fuse system of boron silicate glass kiln, except for clarification of paving brick, also can make the feeding cover. In the "E" glass kiln, make paving bricks or materials around the back wall and feeding mouth.
Zirconium corundum products
Zro2-al2o3 composite ceramics with high strength and toughness can be prepared by using industrial ZrO2 and Al2O3 as raw materials, through ultrafine crushing and strict control of powder size.
The results show that the addition of Al2O3 to ZrO2 matrix can effectively inhibit the growth of ZrO2 grain, which is beneficial to the existence of ZrO2 grain as metastable quadrilateral phase, so as to improve the strength and fracture toughness of the material. When the mass fraction of Al2O3 was 20%, the bending strength and fracture toughness of the composite ceramics reached 676.7mpa and 10MPa/m2 respectively. Phase change toughening and particle dispersion toughening are superimposed on each other to improve the mechanical properties of the composites.
Al2O3 micropowder was prepared by thermal decomposition method, ZrO2 ultrafine powder was prepared by chemical co-precipitation method, and ZrO2/Al2O3 complex ceramic was prepared by appropriate technology. It is believed that the addition of Al2O3 can inhibit the grain growth of ZrO2 and improve the strength and toughness of the matrix. When the mass fraction of Al2O3 reaches 30%, the bending strength and fracture toughness of the composite ceramics fired at 1600℃ are 968MPa and 13.7mpa /m2 respectively.
ZrO2 was added to the refractory material to make corundum - zirconia composite material. When the samples of corundum and zirconia were fired and cooled, ZrO2 underwent phase transition, and a certain number of micro-cracks were formed in the material, which was beneficial to the improvement of mechanical strength and toughness of the material. When the applied amount of ZrO2 is small, the number of micro-cracks in the material is not large, which has little influence on the strength of the rigid jade refractory. When the applied amount is too high (such as reaching the mass fraction of more than 9%), the flexural strength of the material will decrease because of the number of microcracks in the material.
Corundum, synthetic mullite and monoclinal ZrO2 were used as raw materials, and the mixture was formed by isostatic pressing and fired at 1650~1700℃. The bending strength of the sample varies with the temperature as follows: the strength increases before the temperature, and then decreases with the temperature rising after the transition temperature, which is the result of the thermal expansion mismatch between different crystal phases and the partial bridging of microcracks. The transition temperature is between 800 ℃ and 900℃. Due to the martensitic transformation of ZrO2, there are "valleys" at 1000 ℃ and 1200℃, and the valley bottom is at 1100℃.
The addition of ZrO2 has a significant effect on the mechanical properties and microstructure of the samples at high temperature. At low temperature (20~800℃), the strength change after ZrO2 is added depends on two aspects of the microstructure -- the strength of the structure skeleton and the density of microcracks, and the latter is generally dominant. When ZrO2 is about 15%, the uniformly dispersed ZrO2 is filled in the corundum -- mullite skeleton, which plays a certain strengthening role. However, the weakening effect caused by the microcrack generated by martensitic transformation exceeds this strengthening effect, so the strength is reduced. When the ZrO2 quantity increased to 20%~35%, the structure skeleton weakened somewhat and the microcrack density increased, so the strength continued to decline. With the addition of ZrO2 reaching more than 40%, the strength of the structure skeleton has been significantly improved, so the strength has slightly recovered.
At the high temperature stage of 1300~1500℃, most of the microcracks have been closed and passivated, so they have little effect on strengthening. At this point, the strength change is determined by the strengthening effect of structural skeleton strength and grain boundary solid solution. With the addition of ZrO2, the solid solution strength of grain boundary increases, and a small amount of ZrO2 may enter the glass phase of grain boundary, which can improve the viscosity and strengthen to some extent.
In ZrO2 toughened Al2O3 ceramics, ZrO2 particles are introduced by mechanical mixing and grinding. In the sintering process, there is no reaction or recombination between the two substances, but the densification is achieved by surface evaporation and interfacial diffusion at high temperature, which belongs to solid phase sintering. The addition of ZrO2 can promote sintering, and when the sintering time is prolonged, it can hinder the growth of Al2O3 grain and improve the mechanical properties of products at high temperature.
2%TiO2 was added to zirconium corundum, and TiO2 was prefered to form solid melt with ZrO2. However, the formation of solid melt did not prevent the crystal transformation of ZrO2, and ZrO2 was still dominated by m-zro2. TiO2 promoted the development of Al2O3 and ZrO2 grains, which increased the porosity and decreased the strength of the material. The addition of TiO2 reduced the high-temperature linear expansion rate of zirconium corundum, but the linear relationship between thermal expansion rate and temperature was not uniform, and the curve showed a maximum value at 1100℃.
Al2O3/ZrO2 sintered material was prepared by adding ZrO2 into Al2O3 ceramics. This series of ceramic materials have high hardness, good toughness and excellent wear resistance. Can be used for manufacturing tools, plug gauge, sliding bearing, etc. Used in the metallurgical industry as a sliding gate material. A series of theoretical studies on al2o3-zro2 materials have also laid a good foundation for manufacturing high-quality al2o3-zro2-c materials.

