Performance of Unshaped Refractories
The performance of evaluating the operation difficulty of amorphous refractories is called operational performance, also known as construction performance. Operation performance directly affects the construction efficiency and construction quality. Good working performance should mean that the material can complete the construction under the condition of saving time and labor, and can obtain better construction quality. However, different construction methods are used for materials in different states, which have different operating performance requirements, such as good fluidity for castable materials, and good local adhesion rate for plastics. Therefore, the operating properties of amorphous refractory materials include workability, consistency, thixotropy, flow value, spreadability, plasticity, adhesion rate, maxia value, coagulability and hardenability, etc.
workability
It is called workability to measure the difficulty of adding water (or liquid binder) to a dry mixture of amorphous refractories to achieve even mixing. The workability of the mixture is related to the material material, particle size composition and viscosity of the mixing liquid. When the mixture is hard to mix, it needs more mixing energy, especially when adding the liquid binder with higher viscosity, it needs to mix with a high power mixer. On the contrary, easy to mix the mixture mixing, the required mixing energy is smaller, the required power of the mixer is also small. Therefore, according to the power input to the mixer, the ease of blending can be judged. A new rheometer for measuring the rheological properties of amorphous refractories has been developed.
The workability of amorphous refractory can be improved by adjusting its composition (proportion of aggregate to powder, fineness of powder, etc.) and adding dispersant (water reducer). On the other hand, the shape of aggregate particles also has a great influence on the workability. The irregular shape of aggregate, such as flake, columnar and sharp-angle particles, has a large frictional resistance and poor workability when stirred and mixed. However, spherical or near-spherical particles have low frictional resistance and good workability when mixed.
consistency
The standard for evaluating the fluidity of slurry amorphous refractories (e.g., refractory slurry, injection refractories, refractory coatings, etc.) is called consistency. The greater the fluidity, the less the consistency. The fluidity of slurry is closely related to the ratio of solid to liquid in slurry (solid powder - stream suspension). In addition to the factors influencing the solid-liquid ratio, the particle size distribution of the solid powder, the shape of solid particles, the viscosity of the blending liquid and the properties of additives (dispersants or degumming agents) are also closely related to the added amount. In particular, the properties of dispersant (or degumming agent) have a great influence on the amount added, so the solid powder with different properties should be selected with different properties of dispersant (or degumming agent).
The determination of consistency is relatively simple. In the metallurgical industry standard of China (YB/ t512-1993), the test method for the consistency of refractory mud is to measure the consistency by using the depth of the slurry of a certain mass of aluminum cone freely sunk into a container of a certain volume. YB/ t5202-1993 "determination of dense refractory castable consistency and sample preparation method" is to pour slurry into a container of fixed volume and measure the time for slurry to flow out of the outlet of fixed diameter at the bottom of the container to evaluate its consistency. The shorter the outflow time, the smaller the consistency.
Liquidity (current value)
A technical indicator of the difficulty of construction of vibration pouring or artesian pouring of refractory castables is expressed by flow value. The larger the flow value of the castable, the easier it is to fill the model and smooth the surface, and the more uniform the structure of the construction body, the more convenient the construction. Therefore, flow value is a very important performance index of castable.
However, the factors that affect the flow value of pouring material are very large, including the particle size distribution of pouring material, the particle morphology of aggregate, the properties and addition amount of dispersant, the amount of water added and the mixing and stirring process. Particle size distribution and dispersant properties are the main influencing factors. Pouring material of the particle size distribution is controlled by particle size distribution coefficient q value, shakes the castable size distribution coefficient q value of construction generally take 0.26 ~ 0.35, and their construction of castable q value usually take 0.21 ~ 0.26, dispersant according to castable to choose of matrix powder, inorganic electrolytes dispersant, useful also useful organic polymer surface active agent, addition amount is commonly 0.05% ~ 0.2%.
Most of the measurement of the flow value of castable material is by means of a tablelometer. Determination method is: will a high for a first 60 mm, inner diameter is 70 mm, upper side of mouth diameter is 100 mm with concentric circles of the truncated cone canister jump table scale glass desktop, and then mixing pour castable truncated cone tube, surface smooth, smoke to cone tube, a jumping up and down at a speed of 15 times per second, from two directions perpendicular to determine the diameter of the castable spread out on the glass plate, take the average Dmean, press type calculation flow value f. v.
f·v=(Dmean-100)/100
For the artesian castable, the flow value measurement procedure is similar to the above except that the pulsation and vibration are not given. After the conical cylinder is removed, the diameter after the artesian spread of the castable is measured again after 2~3min. The calculation method is the same.
spreadability
An indicator of the difficulty of applying a spatula to a refractory product or to a refractory masonry surface of a slurry or paste refractory material (refractory mud, refractory daub) is called spreadability. For this kind of slurry or paste refractory, generally required to have a certain degree of viscoplastic, in order to make the coating material in the process of spreading easy and uniform without drying (good water retention) or flowing.
This kind of pulp or paste refractory spreadability mainly additive to adjust, the stand or fall of the admixtures such as plasticizer, water retention agent, such as plastic clay, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, lignin sulfonate, dextrin, silica sol, carboxymethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose have plasticizing effect and water.
There is no exact way to determine the spread of the mud, most of which is based on the feeling of the builder, but in the case of refractory mud, it is measured by the time the mud applied to the masonry allows rubbing back and forth. China metallurgical industry standard YB/T5122-1993 "test method for refractory slurry cementing time", for 320 ~ 380 refractory slurry with consistency, coated in 230 mm x 114 mm standard brick, and put on the surface of the brick is 3 mm in diameter of two stick of isolation (parallel, spacing is 170 mm), and on the overlapping we put a piece of standard brick, brick of above knead move back and forth, until not knead move when the time for bonding time, loss of spreadability and now.
plasticity
Block refractory clay can produce deformation without cracking or collapse under the action of external forces. The shape after deformation can be maintained after the removal of external forces is called plasticity. Plasticity is expressed by plasticity index. Plasticity index is a very important index to measure the plasticity of materials or the difficulty of material construction.
Different materials (e.g. malleable clays and refractory plastics) are used to measure their malleability with different instruments and methods. Chinese metallurgical industry standard YB/ t5119-1993 "test method for clay and high-alumina refractory plastic plasticity index", the instruments used are shown in figure 17-4. The test procedure is as follows: 50mm in diameter and (50±2) mm in height shall be made of the available plastics on the measuring instrument according to the standard method, and then the samples shall be placed on the cushion of the instrument to measure the height L0 (mm) of the samples before impact. After three times of heavy hammer impact on the instrument, the height L value of the samples after impact shall be measured. Press the formula below to calculate the plasticity index Wa%.
Wa(%)=(L0-L)/L0
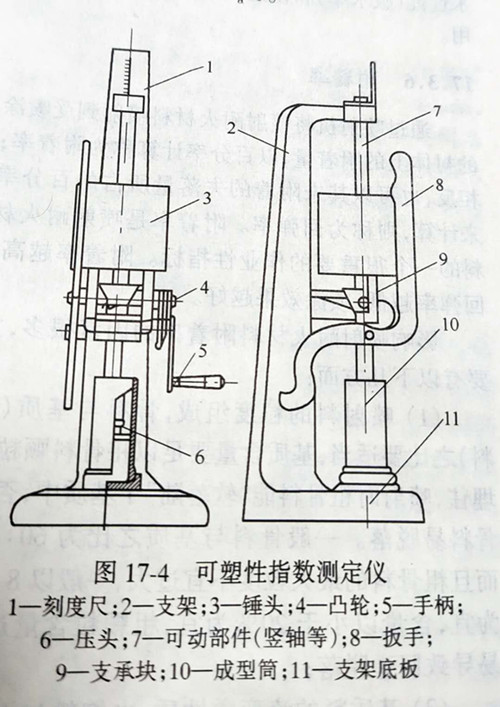
According to this method, the plasticity index of refractory plastics is between 15% and 40%. There are many factors influencing the plasticity index of refractory plastics, but the main influencing factors are:
(1) the ratio of coarse aggregate to fine powder in plasticizable clay is greater than 100cm and smaller than 100cm, which generally means that the plasticity increases with the increase of fine powder content. This is because the increase of fineness, the increase of contact points between particles, easy to displacement caused by;
(2) the volume ratio between solid and liquid phase, but the water content of plastic has a certain range, with different properties of powder general fluctuation between 9%~13% (mass ratio), water content is too low or too high are difficult to obtain the appropriate plasticity index. Water plays a certain lubricating role in plastic under the action of external forces, but also can form a "liquid bridge" between the particles in plastic after deformation, under the action of van der Waals gravity and capillary force between the particles to maintain the shape of plastic after deformation;
(3) the properties and addition amount of plasticizer materials (such as plastic clay) or plasticizer generally require that plasticizer materials have appropriate water retention properties (water absorption) and play a lubricating role between aggregate particles.

