Sodium Silicate Combined Castable
Water glass as a binder, and refractory aggregate and admixture made of castable refractory material is called water glass combined castable. Water glass is alkali metal silicate, chemical general formula is R2O·nSiO2·mH2O,R2O refers to alkali metal oxide, sodium silicate water glass, potassium silicate water glass, quaternary amine silicate water glass and sodium potassium silicate water glass. However, sodium silicate glass is widely used in amorphous refractories. Sodium silicate water glass can be divided into neutral water glass (M not less than 3) and alkaline water glass (M less than 3.0) according to its modulus M (referring to the molar ratio of SiO2 and Na2O). However, this is just a customary classification.
Water glass is a kind of strong base and weak acid salt, which is easy to hydrolyze in water, and its hydrolytic reaction is complicated. The hydrolytic reaction of sodium silicate water glass can be summarized as follows:
Na2O · nSiO2 + naoh mH2O - > 2 + nSiO2 H2O (m - 1)
And the NaOH will further ionize into Na++OH-, so that the molten water glass is alkaline. The aqueous solution is actually a colloidal solution. The physical properties of the sodium silicate is modulus M, density and viscosity eta D to measure, its modulus calculation formula is as follows:
M = 1.023 SiO2 / Na2O
Where, SiO2 and Na2O refer to the percentage of SiO2 and Na2O in water glass respectively. Density can Be measured by a pomerometer. The relationship between density D and baume (Be ') is as follows:
D = 145 / (145 - DHS Be ') or DHS Be/D '= 145-145
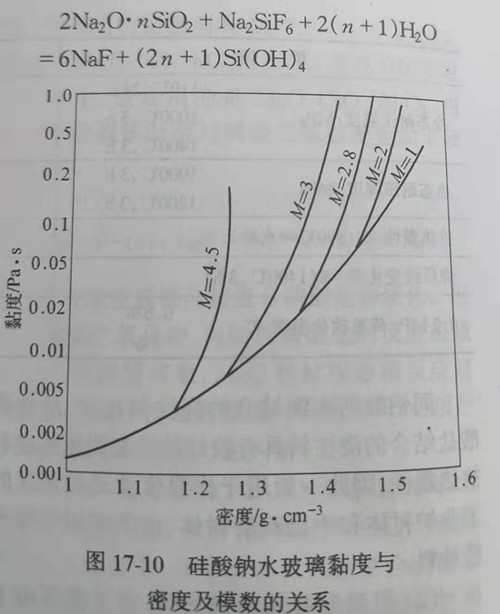
When using water glass solution as binder for castable, its performance is mainly determined by viscosity, which varies with the density and modulus of water glass, as shown in figure 17-10.
Water glass can be used as a binder for both acidic (e.g., siliceous, waxy) and neutral (clay, high aluminum) castables and as a binder for alkaline (e.g., magnesia-magnesia-chrome, magnesia-aluminum) castables. For acid and neutral refractory castable binder, coagulant must be added in order to coagulate and harden. Sodium fluorosilicate (Na2SiF6) is generally used as a coagulant, and its coagulant reaction is as follows:
As the reaction proceeds, the silicate sol becomes a gel and precipitates out, forming a solid hardening product. In addition to sodium fluorosilicate, other substances that can be used as coagulants for water glass are polysodium phosphate, sodium phosphate, aluminum chloride, CO2, Ba(OH)2, Ca(OH)2, acetic acid ethanol, glyoxal, etc.
When using water glass as binder for alkaline castable, no coagulant can be added, because MgO in alkaline refractory will react with water glass to produce hydrated magnesium silicate, which will coagulate and harden.
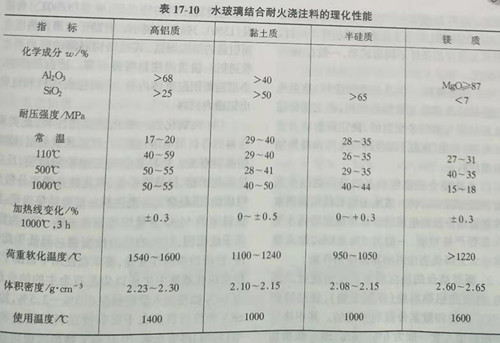
The particle size composition of water-glass bonded refractory castable aggregate is similar to that of ordinary cement-bonded castable, with aggregate greater than 100xm accounting for 60%~70% and powder accounting for 30%~40%. The water-glass modulus adopted is 2.3-3.0, the density is 1.20-1.35g /cm3, the content is 13%~15%, and the content of sodium fluosilicate coagulant is 10%~15% of that of water-glass. Table 17-10 shows the general physical and chemical properties of water-glass bonded castables.
Because of the Na2O in the water-glass binder, the fireproof and high-temperature performance of the refractory castable will be greatly reduced, so the water-glass aluminum silicate (clay and high aluminum) castable can only be used below 1300℃ in general, mostly used as acid and alkali resistant castable. The aluminum magnesium castable combined with water glass can be used as the inner lining of non-continuous casting, non-refined ordinary ladle and the inner lining of steel outlet groove. Water glass combined with alkaline castable can be used as hot repair material for metallurgical furnaces, steel outlet grooves and lining of some induction furnaces.